Clinical study on the surgical treatment of atypical Lisfranc joint complex injury
- PMID: 33083398
- PMCID: PMC7559651
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i19.4388
Clinical study on the surgical treatment of atypical Lisfranc joint complex injury
Abstract
Background: Lisfranc injuries have not received much attention by orthopedic doctors in the past, and there is little related research on the diagnosis and treatment of these injuries. In recent years with the rise in foot and ankle surgery, doctors are now paying more attention to this type of injury. However, there is still a high rate of missed diagnosis due to insufficient attention causing treatment delays or inadequate treatments, which eventually result in greater sequelae; including long-term pain, arthritis, foot deformity etc. In particular, for cases with a mild Lisfranc joint complex injury, the incidence of sequelae is higher.
Aim: To select an active surgical treatment for an atypical Lisfranc joint complex injury and to evaluate the clinical efficacy of the surgical treatment.
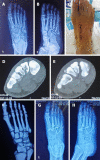
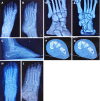
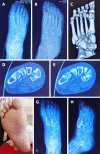
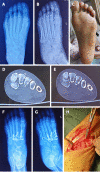
Methods: The clinical data of 18 patients, including 10 males and 8 females aged 20-64 years with Lisfranc injuries treated in our department from January 2017 to September 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients were treated with an open reduction and internal fixation method using locking titanium mini-plates and hollow screws or Kirschner wires. X-ray images were taken and follow-up was performed monthly after the operation; the internal fixation was then removed 4-5 mo after the operation; and the American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score was used for evaluation on the last follow-up.
Results: All patients were followed up for 6-12 mo. A good/excellent AOFAS score was observed in 88.9% of patients.
Conclusion: For atypical Lisfranc joint complex injuries, active open reduction and internal fixation can be performed to enable patients to obtain a good prognosis and satisfactory functional recovery.
Keywords: Atypical Lisfranc injury; Avulsion fracture; Computed tomography; Lisfranc joint complex injury; Open reduction and internal fixation; Stress test.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: This research was not affected by external sources being it personal, commercial, political, intellectual or religious interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hardcastle PH, Reschauer R, Kutscha-Lissberg E, Schoffmann W. Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint. Incidence, classification and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982;64:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Stødle AH, Hvaal KH, Enger M, Brøgger H, Madsen JE, Ellingsen Husebye E. Lisfranc injuries: Incidence, mechanisms of injury and predictors of instability. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;26:535–540. - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar BS, An VVG, Oitment C, Myerson M. Subtle Lisfranc Injuries: A Topical Review and Modification of the Classification System. Orthopedics. 2018;41:e168–e175. - PubMed
-
- Krause F, Schmid T, Weber M. Current Swiss Techniques in Management of Lisfranc Injuries of the Foot. Foot Ankle Clin. 2016;21:335–350. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

