Comprehensive Analysis of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs in Patients with Senile Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
- PMID: 33083467
- PMCID: PMC7556071
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4951251
Comprehensive Analysis of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs in Patients with Senile Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
Abstract
Aim: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been found to contribute to the regulation of many diseases and are abundantly expressed in various organisms. The present study is aimed at systematically characterizing the circRNA expression profiles in patients with senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF) and predicting the potential functions of the regulatory networks correlated with these differentially expressed circRNAs.
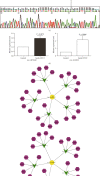
Methods: The circRNA expression profile in patients with senile OVCF was explored by using RNA sequencing. The prediction of the enriched signaling pathways and circRNA-miRNA networks was conducted by bioinformatics analysis. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to validate the selected differentially expressed circRNAs from 20 patients with senile OVCF relative to 20 matched healthy controls.
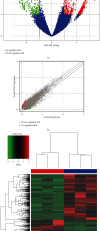
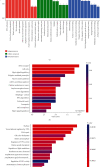
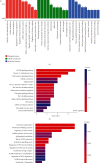
Results: A total of 884 differentially expressed circRNAs were identified, of which 554 were upregulated and 330 were downregulated. The top 15 signaling pathways associated with these differentially expressed circRNAs were predicted. The result of qRT-PCR of the selected circRNAs was consistent with RNA sequencing.
Conclusions: CircRNAs are differentially expressed in patients with senile OVCF, which might contribute to the pathophysiological mechanism of senile osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2020 Xiaocong Yao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jacobs E., Senden R., McCrum C., van Rhijn L. W., Meijer K., Willems P. C. Effect of a semirigid thoracolumbar orthosis on gait and sagittal alignment in patients with an osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2019;14:671–680. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S199853. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

