Fusion of medical imaging and electronic health records using deep learning: a systematic review and implementation guidelines
- PMID: 33083571
- PMCID: PMC7567861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-020-00341-z
Fusion of medical imaging and electronic health records using deep learning: a systematic review and implementation guidelines
Abstract
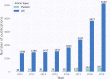
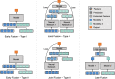
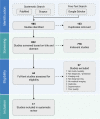
Advancements in deep learning techniques carry the potential to make significant contributions to healthcare, particularly in fields that utilize medical imaging for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment decisions. The current state-of-the-art deep learning models for radiology applications consider only pixel-value information without data informing clinical context. Yet in practice, pertinent and accurate non-imaging data based on the clinical history and laboratory data enable physicians to interpret imaging findings in the appropriate clinical context, leading to a higher diagnostic accuracy, informative clinical decision making, and improved patient outcomes. To achieve a similar goal using deep learning, medical imaging pixel-based models must also achieve the capability to process contextual data from electronic health records (EHR) in addition to pixel data. In this paper, we describe different data fusion techniques that can be applied to combine medical imaging with EHR, and systematically review medical data fusion literature published between 2012 and 2020. We conducted a systematic search on PubMed and Scopus for original research articles leveraging deep learning for fusion of multimodality data. In total, we screened 985 studies and extracted data from 17 papers. By means of this systematic review, we present current knowledge, summarize important results and provide implementation guidelines to serve as a reference for researchers interested in the application of multimodal fusion in medical imaging.
Keywords: Data integration; Machine learning; Medical imaging.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence-based methods for fusion of electronic health records and imaging data.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 26;12(1):17981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22514-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36289266 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven modeling and prediction of blood glucose dynamics: Machine learning applications in type 1 diabetes.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Jul;98:109-134. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31383477 Review.
-
Multimodal deep learning for liver cancer applications: a scoping review.Front Artif Intell. 2023 Oct 27;6:1247195. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1247195. eCollection 2023. Front Artif Intell. 2023. PMID: 37965284 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on electronic health records multimodal data fusion based on deep learning].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Oct 25;41(5):1062-1071. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202310011. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39462676 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Advancements in Medical Radiology Through Multimodal Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Overview.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;12(5):477. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12050477. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving and Novel Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Thoracic Imaging.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;14(13):1456. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131456. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FedSepsis: A Federated Multi-Modal Deep Learning-Based Internet of Medical Things Application for Early Detection of Sepsis from Electronic Health Records Using Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano Devices.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 14;23(2):970. doi: 10.3390/s23020970. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679766 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-center retrospective cohort study applying deep learning to electrocardiograms to identify left heart valvular dysfunction.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Feb 14;3(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00240-w. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36788316 Free PMC article.
-
Pareto optimization of deep networks for COVID-19 diagnosis from chest X-rays.Pattern Recognit. 2022 Jan;121:108242. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108242. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Pattern Recognit. 2022. PMID: 34393277 Free PMC article.
-
DeepCOVID-Fuse: A Multi-Modality Deep Learning Model Fusing Chest X-rays and Clinical Variables to Predict COVID-19 Risk Levels.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 May 5;10(5):556. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10050556. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237626 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

