A whole-genome worldwide molecular epidemiology approach for contagious caprine pleuropneumonia
- PMID: 33083610
- PMCID: PMC7550919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05146
A whole-genome worldwide molecular epidemiology approach for contagious caprine pleuropneumonia
Abstract
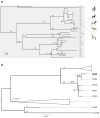
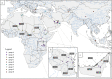
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia is an infectious and contagious disease affecting goats and wildlife ruminants, mostly in Africa and Asia. It is caused by a mycoplasma, Mycoplasma capricolum susbp. capripneumoniae, which is very fastidious. This may be the reason why there are few reports of its isolation and characterization. This study describes the development of a whole genome typing strategy based on sequencing reads assemblies on a reference genome (Abomsa, GenBank accession LM995445) and extraction of informative single nucleotide polymorphism. FASTA sequences inferred from the variant calling files were used to establish a comprehensive phylogenetic tree based on 2880 SNPs. This tree included a total of 34 strains originating from all the regions where CCPP has been detected, as well as strains isolated from wildlife. A recent isolate from West-Niger was positioned closely to another 1995 East-Niger isolate, an indication that CCPP may be extending westward in Africa. Six 2013 Tanzanian isolates had identical sequences in spite of diverse geographical origins. This could be explained by the clonal expansion of a virulent strain at that time in East Africa. Although all strains isolated from wildlife in the Middle East were in the same phylogenetic group, this may not sign an adaptation to new hosts. The most probable explanation for wildlife contamination remains the contact with goats. This strategy will easily accommodate new data in the near future and should become a gold-standard high-resolution typing procedure for the surveillance of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia; Evolutionary biology; Genetics; Microbiology; Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae; Veterinary medicine; Whole genome phylogeny.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A specific PCR for the identification of Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae, the causative agent of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP).Vet Microbiol. 2004 Nov 30;104(1-2):125-32. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.08.006. Vet Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15530747
-
A molecular epidemiological investigation of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in goats and captive Arabian sand gazelle (Gazella marica) in Oman.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Apr 25;20(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03969-1. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38664764 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evolution of Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae strains and molecular epidemiology of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia by sequencing of locus H2.Vet Microbiol. 2002 Mar 1;85(2):111-23. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(01)00509-0. Vet Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11844618
-
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia: new aspects of an old disease.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2012 Jun;59(3):189-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2011.01262.x. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2012. PMID: 21951488 Review.
-
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP): A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence in sheep and goats.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 May;68(3):1332-1344. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13794. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 33448706
Cited by
-
Multi-locus sequence analysis reveals great genetic diversity among Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae strains in Asia.Vet Res. 2022 Nov 14;53(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01107-z. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36376915 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the control measures for category A diseases of Animal Health Law: Contagious Caprine Pleuropneumonia.EFSA J. 2022 Jan 25;20(1):e07068. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7068. eCollection 2022 Jan. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35106092 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the control measures for category A diseases of Animal Health Law: Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia.EFSA J. 2022 Jan 21;20(1):e07067. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7067. eCollection 2022 Jan. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35079288 Free PMC article.
-
A toolbox for manipulating the genome of the major goat pathogen, Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Jan;170(1):001423. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001423. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 38193814 Free PMC article.
-
Immune and Oxidative Response against Sonicated Antigen of Mycoplasma capricolum subspecies capripneumonia-A Causative Agent of Contagious Caprine Pleuropneumonia.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1634. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081634. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36014052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arif A., Schulz J., Thiaucourt F., Taha A., Hammer S. Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia outbreak in captive wild ungulates at Al Wabra Wildlife Preservation, State of Qatar. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2007;38:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Bolske G., Johansson K.E., Heinonen R., Panvuga P.A., Twinamasiko E. Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in Uganda and isolation of Mycoplasma capricolum subspecies capripneumoniae from goats and sheep. Vet. Rec. 1995;137:594. - PubMed
-
- Botes A., Peyrot B.M., Olivier A.J., Burger W.P., Bellstedt D.U. Identification of three novel mycoplasma species from ostriches in South Africa. Vet. Microbiol. 2005;111:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Chaber A., Lignereux L., Qassimi M.A., Saegerman C., Manso-Silvan L., Dupuy V., Thiaucourt F. Fatal transmission of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia to an Arabian oryx (Oryx leucoryx) Vet. Microbiol. 2014;173:156–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

