Exome Sequencing Implicates Impaired GABA Signaling and Neuronal Ion Transport in Trigeminal Neuralgia
- PMID: 33083721
- PMCID: PMC7554653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101552
Exome Sequencing Implicates Impaired GABA Signaling and Neuronal Ion Transport in Trigeminal Neuralgia
Abstract
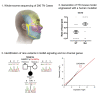
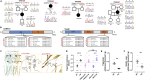
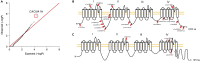
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a common, debilitating neuropathic face pain syndrome often resistant to therapy. The familial clustering of TN cases suggests that genetic factors play a role in disease pathogenesis. However, no unbiased, large-scale genomic study of TN has been performed to date. Analysis of 290 whole exome-sequenced TN probands, including 20 multiplex kindreds and 70 parent-offspring trios, revealed enrichment of rare, damaging variants in GABA receptor-binding genes in cases. Mice engineered with a TN-associated de novo mutation (p.Cys188Trp) in the GABAA receptor Cl- channel γ-1 subunit (GABRG1) exhibited trigeminal mechanical allodynia and face pain behavior. Other TN probands harbored rare damaging variants in Na+ and Ca+ channels, including a significant variant burden in the α-1H subunit of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel Cav3.2 (CACNA1H). These results provide exome-level insight into TN and implicate genetically encoded impairment of GABA signaling and neuronal ion transport in TN pathogenesis.
Keywords: Genomics; Neuroscience; Structural Biology.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ackerman M.J., Siu B.L., Sturner W.Q., Tester D.J., Valdivia C.R., Makielski J.C., Towbin J.A. Postmortem molecular analysis of SCN5A defects in sudden infant death syndrome. JAMA. 2001;286:2264–2269. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed O.L., Akinyele O.A., Akindayo A.O., Bamidele K. Management of trigeminal neuralgia using amitriptyline and pregablin combination therapy. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2012;15:201–203.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

