Shaping Polyclonal Responses via Antigen-Mediated Antibody Interference
- PMID: 33083735
- PMCID: PMC7530306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101568
Shaping Polyclonal Responses via Antigen-Mediated Antibody Interference
Abstract
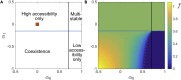
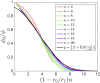
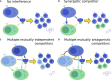
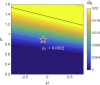
Broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) recognize conserved features of rapidly mutating pathogens and confer universal protection, but they emerge rarely in natural infection. Increasing evidence indicates that seemingly passive antibodies may interfere with natural selection of B cells. Yet, how such interference modulates polyclonal responses is unknown. Here we provide a framework for understanding the role of antibody interference-mediated by multi-epitope antigens-in shaping B cell clonal makeup and the fate of bnAb lineages. We find that, under heterogeneous interference, clones with different intrinsic fitness can collectively persist. Furthermore, antagonism among fit clones (specific for variable epitopes) promotes expansion of unfit clones (targeting conserved epitopes), at the cost of repertoire potency. This trade-off, however, can be alleviated by synergy toward the unfit. Our results provide a physical basis for antigen-mediated clonal interactions, stress system-level impacts of molecular synergy and antagonism, and offer principles to amplify naturally rare clones.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Immunology; Mathematical Biosciences.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Bachmann M., Kalinke U., Althage A., Freer G., Burkhart C., Roost H.-P., Aguet M., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. The role of antibody concentration and avidity in antiviral protection. Science. 1997;276:2024–2027. - PubMed
-
- Bunin G. Ecological communities with lotka-volterra dynamics. Phys. Rev. E. 2017;95:042414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

