This is a preprint.
IgM autoantibodies recognizing ACE2 are associated with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 33083808
- PMCID: PMC7574257
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.10.13.20211664
IgM autoantibodies recognizing ACE2 are associated with severe COVID-19
Update in
-
IgM anti-ACE2 autoantibodies in severe COVID-19 activate complement and perturb vascular endothelial function.JCI Insight. 2022 May 9;7(9):e158362. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.158362. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35349483 Free PMC article.
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces severe disease in a subpopulation of patients, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We demonstrate robust IgM autoantibodies that recognize angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) in 18/66 (27%) patients with severe COVID-19, which are rare (2/52; 3.8%) in hospitalized patients who are not ventilated. The antibodies do not undergo class-switching to IgG, suggesting a T-independent antibody response. Purified IgM from anti-ACE2 patients activates complement. Pathological analysis of lung obtained at autopsy shows endothelial cell staining for IgM in blood vessels in some patients. We propose that vascular endothelial ACE2 expression focuses the pathogenic effects of these autoantibodies on blood vessels, and contributes to the angiocentric pathology observed in some severe COVID-19 patients. These findings may have predictive and therapeutic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


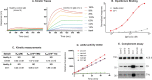
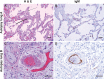
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 579, 270–273 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garibaldi B. T., Fiksel J., Muschelli J., Robinson M. L., Rouhizadeh M., Perin J., Schumock G., Nagy P., Gray J. H., Malapati H., Ghobadi-Krueger M., Niessen T. M., Kim B. S., Hill P. M., Ahmed M. S., Dobkin E. D., Blanding R., Abele J., Woods B., Harkness K., Thiemann D. R., Bowring M. G., Shah A. B., Wang M.-C., Bandeen-Roche K., Rosen A., Zeger S. L., Gupta A., Patient Trajectories Among Persons Hospitalized for COVID-19 : A Cohort Study. Annals of Internal Medicine (2020), doi: 10.7326/M20-3905 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richardson S., Hirsch J. S., Narasimhan M., Crawford J. M., McGinn T., Davidson K. W., and the N. C.−19 R. Consortium, Barnaby D. P., Becker L. B., Chelico J. D., Cohen S. L., Cookingham J., Coppa K., Diefenbach M. A., Dominello A. J., Duer-Hefele J., Falzon L., Gitlin J., Hajizadeh N., Harvin T. G., Hirschwerk D. A., Kim E. J., Kozel Z. M., Marrast L. M., Mogavero J. N., Osorio G. A., Qiu M., Zanos T. P., Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 323, 2052–2059 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuri-Cervantes L., Pampena M. B., Meng W., Rosenfeld A. M., Ittner C. A. G., Weisman A. R., Agyekum R. S., Mathew D., Baxter A. E., Vella L. A., Kuthuru O., Apostolidis S. A., Bershaw L., Dougherty J., Greenplate A. R., Pattekar A., Kim J., Han N., Gouma S., Weirick M. E., Arevalo C. P., Bolton M. J., Goodwin E. C., Anderson E. M., Hensley S. E., Jones T. K., Mangalmurti N. S., Prak E. T. L., Wherry E. J., Meyer N. J., Betts M. R., Comprehensive mapping of immune perturbations associated with severe COVID-19. Science Immunology. 5 (2020), doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd7114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lucas C., Wong P., Klein J., Castro T. B. R., Silva J., Sundaram M., Ellingson M. K., Mao T., Oh J. E., Israelow B., Takahashi T., Tokuyama M., Lu P., Venkataraman A., Park A., Mohanty S., Wang H., Wyllie A. L., Vogels C. B. F., Earnest R., Lapidus S., Ott I. M., Moore A. J., Muenker M. C., Fournier J. B., Campbell M., Odio C. D., Casanovas-Massana A., Herbst R., Shaw A. C., Medzhitov R., Schulz W. L., Grubaugh N. D., Cruz C. D., Farhadian S., Ko A. I., Omer S. B., Iwasaki A., Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19. Nature. 584, 463–469 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
