Conditional knockdown of integrin beta-3 reveals its involvement in osteolytic and soft tissue lesions of breast cancer skeletal metastasis
- PMID: 33083904
- PMCID: PMC7817553
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03428-y
Conditional knockdown of integrin beta-3 reveals its involvement in osteolytic and soft tissue lesions of breast cancer skeletal metastasis
Abstract
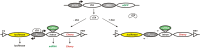
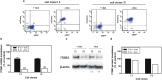
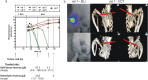
Integrin β3 (ITGB3) is probably related to skeletal metastasis, which is the most frequent complication in breast cancer progression. We aimed to define its role and suitability as target for anti-metastatic therapy. We generated two MDA-MB-231 cell clones with conditional miRNA-mediated ITGB3 knockdown for analyzing the resulting effects in vitro regarding mRNA expression, proliferation and migration, as well the impact on skeletal metastasis in a nude rat model. Furthermore, ITGB3 levels were analyzed in exosomes from plasma of rats with skeletal metastases, and from MDA-MB-231 cells incubated with these vesicles, as well as from exosomes secreted by cells with conditional ITGB3 knockdown. This inhibition of ITGB3 expression decreased cellular proliferation and more distinctly inhibited cellular migration. Reduction and even complete remissions of respective soft tissue and osteolytic lesions were detected after ITGB3 knockdown in vivo. Furthermore, ITGB3 levels were increased in exosomes isolated from plasma of rats harboring MDA-MB-231 lesions as well as in respective cells incubated with these vesicles in vitro. ITGB3 was distinctly decreased in exosomes from cells with ITGB3 knockdown. The observed in vitro and in vivo anti-ITGB3 effects can be explained by downregulation of specific genes, which have roles in angiogenesis (NPTN, RRM2), tumor growth (NPTN), energy metabolism (ISCA1), cytokinesis (SEPT11), migration (RRM2, STX6), cell proliferation, invasiveness, senescence, tumorigenesis (RRM2) and vesicle trafficking (SEPT11, STX6). ITGB3 has a role in breast cancer skeletal metastasis via gene expression modulation, as mirrored for ITGB3 in exosomes, thus it could serve as target for anti-metastatic therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Conditional ITGB3 knockdown; Doxycycline; Integrins; Skeletal metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
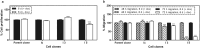
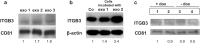

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Bisphosphonates for breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Feb 15;(2):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub3. PMID: 16034900 Updated.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Bisphosphonates for breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub2. PMID: 11869664 Updated.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.Clin Proteomics. 2024 Oct 9;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12014-024-09510-8. Clin Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 39385083 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX2 promotes the suppression of osteoblast function and enhancement of osteoclast activity by multiple myeloma cells.Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 10;40(4):115. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01960-8. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36897488 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous Regeneration Mechanism of β-Sheet Silk Fibroin in a Rat Burn Wound Healing Model.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;13(20):3537. doi: 10.3390/polym13203537. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685296 Free PMC article.
-
The Osteoclast Traces the Route to Bone Tumors and Metastases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 13;10:886305. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.886305. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic markers of thrombophilia as predictors of outcome in colorectal cancer.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jun;58(5):663-678. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03106-1. Epub 2025 May 27. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40425987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauerle T, Komljenovic D, Merz M, Berger MR, Goodman SL, Semmler W (2011) Cilengitide inhibits progression of experimental breast cancer bone metastases as imaged noninvasively using VCT, MRI and DCE-MRI in a longitudinal in vivo study. Int J Cancer 128(10):2453–2462. 10.1002/ijc.25563 - PubMed
-
- Cozar-Castellano I, del Valle MM, Trujillo E, Arteaga MF, Gonzalez T, Martin-Vasallo P, Avila J (2004) hIscA: a protein implicated in the biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters. Biochem Biophys Acta 1700(2):179–188. 10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.05.004 - PubMed
-
- Das V, Kalyan G, Hazra S, Pal M (2018) Understanding the role of structural integrity and differential expression of integrin profiling to identify potential therapeutic targets in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 233(1):168–185. 10.1002/jcp.25821 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

