Coronavirus: proteomics analysis of chicken kidney tissue infected with variant 2 (IS-1494)-like avian infectious bronchitis virus
- PMID: 33083914
- PMCID: PMC7574675
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-020-04845-7
Coronavirus: proteomics analysis of chicken kidney tissue infected with variant 2 (IS-1494)-like avian infectious bronchitis virus
Abstract
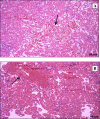
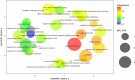
Avian infectious bronchitis virus is one of the most important gammacoronaviruses, which causes a highly contagious disease. In this study, we investigated changes in the proteome of kidney tissue of specific-pathogen-free (SPF) chickens that were infected with an isolate of the nephrotropic variant 2 genotype (IS/1494/06) of avian coronavirus. Twenty 1-day-old SPF White Leghorn chickens were randomly divided into two groups, each comprising 10 chickens, which were kept in separate positive-pressure isolators. Chickens in group A served as a virus-free control group up to the end of the experiment, whereas chickens in group B were inoculated with 0.1 ml of 104.5 EID50 of the IBV/chicken/Iran/UTIVO-C/2014 isolate of IBV, and kidney tissue samples were collected at 2 and 7 days post-inoculation (dpi) from both groups. Sequencing of five protein spots at 2 dpi and 22 spots at 7 dpi that showed differential expression by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2DE) along with fold change greater than 2 was done by MS-MALDI/TOF/TOF. Furthermore, the corresponding protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks at 2 and 7 dpi were identified to develop a detailed understanding of the mechanism of molecular pathogenesis. Topological graph analysis of this undirected PPI network revealed the effect of 10 genes in the 2 dpi PPI network and nine genes in the 7 dpi PPI network during virus pathogenesis. Proteins that were found by 2DE analysis and MS/TOF-TOF mass spectrometry to be down- or upregulated were subjected to PPI network analysis to identify interactions with other cellular components. The results show that cellular metabolism was altered due to viral infection. Additionally, multifunctional heat shock proteins with a significant role in host cell survival may be employed circuitously by the virus to reach its target. The data from this study suggest that the process of pathogenesis that occurs during avian coronavirus infection involves the regulation of vital cellular processes and the gradual disruption of critical cellular functions.
Figures
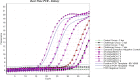
 , 2 dpi control group;
, 2 dpi control group;  , 2 dpi infected group;
, 2 dpi infected group;  , 7 dpi control group;
, 7 dpi control group;  , 7 dpi infected group;
, 7 dpi infected group;  , negative RT-PCR standard;
, negative RT-PCR standard;  , standard 104;
, standard 104;  , standard 105;
, standard 105;  , standard 106;
, standard 106;  , standard 107;
, standard 107;  , standard 108;
, standard 108;  , positive RT-PCR standard
, positive RT-PCR standard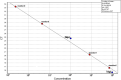





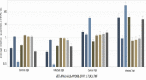
References
-
- Schalk AF, Hawn MC. An apparently new respiratory disease of baby chicks. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1931;78(19):413–422.
-
- Jackwood MW. Review of infectious bronchitis virus around the world invited review—review of infectious bronchitis virus around the world. Avian Dis. 2012;56(4):634–641. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

