The correlation between Jun N-terminal kinase pathway-associated phosphatase and Th1 cell or Th17 cell in sepsis and their potential roles in clinical sepsis management
- PMID: 33083958
- PMCID: PMC8302537
- DOI: 10.1007/s11845-020-02382-5
The correlation between Jun N-terminal kinase pathway-associated phosphatase and Th1 cell or Th17 cell in sepsis and their potential roles in clinical sepsis management
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the association between Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway-associated phosphatase (JKAP) and T helper type 1 (Th1) cell or Th17 cell, and their clinical values in sepsis patients.
Methods: Totally 125 sepsis patients and 100 healthy subjects as controls were included. Peripheral blood was extracted from each sepsis patient and each control, then serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) were separated. JKAP and inflammatory cytokines were detected in serum by ELISA; Th1 cell or Th17 cell proportion was detected in PBMC using flow cytometry.
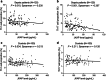
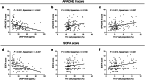
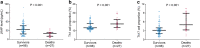
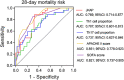
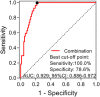
Results: JKAP level was downregulated while Th1 and Th17 cell proportions were upregulated in sepsis patients compared with controls. JKAP level negatively correlated with Th1 cell proportion in sepsis patients and controls, while was only negatively associated with Th17 cell proportion in sepsis patients but not in controls. In sepsis patients, JKAP level negatively associated with TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 expressions. Meanwhile, JKAP level negatively but Th17 cell proportion positively correlated with acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores; however, Th1 cell proportion only positively associated with APACHE II score but not SOFA score. Additionally, JKAP level was reduced, while Th1 and Th17 cell proportions were increased in septic deaths compared with survivors. Multivariate logistic regression model disclosed that JKAP level and Th17 cell proportion independently predicted 28-day mortality.
Conclusion: Blood JKAP correlates with decreased Th1 and Th17 cells, also associates with reduced inflammatory cytokines, disease severity, and favorable outcome in sepsis patients.
Keywords: Inflammatory cytokines; Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway-associated phosphatase; Mortality; Sepsis; T helper type 1; T helper type 17.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
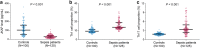

Similar articles
-
JKAP relates to disease risk, severity, and Th1 and Th17 differentiation in Parkinson's disease.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021 Sep;8(9):1786-1795. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51420. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34289265 Free PMC article.
-
JNK pathway-associated phosphatase in acute ischemic stroke patients: Its correlation with T helper cells, clinical properties, and recurrence risk.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Aug;36(8):e24535. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24535. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35808912 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating JNK pathway-associated phosphatase: A novel biomarker correlates with Th17 cells, acute exacerbation risk, and severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24153. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24153. Epub 2021 Dec 16. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34918391 Free PMC article.
-
JNK pathway-associated phosphatase illustrates low expression and negative correlations with inflammation, disease activity, and T-helper 17 cells in inflammatory bowel disease children.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24488. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24488. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35908771 Free PMC article.
-
JKAP, Th1 cells, and Th17 cells are dysregulated and inter-correlated, among them JKAP and Th17 cells relate to cognitive impairment progression in Alzheimer's disease patients.Ir J Med Sci. 2022 Aug;191(4):1855-1861. doi: 10.1007/s11845-021-02749-2. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Ir J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34595688
Cited by
-
Measurement of synovium and serum dual specificity phosphatase 22 level: Their inter-correlation and potency as biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24111. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24111. Epub 2021 Nov 22. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34811816 Free PMC article.
-
JKAP relates to disease risk, severity, and Th1 and Th17 differentiation in Parkinson's disease.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021 Sep;8(9):1786-1795. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51420. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34289265 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-451a and Th1/Th2 ratio inform inflammation, septic organ injury, and mortality risk in sepsis patients.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 4;13:947139. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.947139. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35992658 Free PMC article.
-
Th17, rather than Th1 cell proportion, is closely correlated with elevated disease severity, higher inflammation level, and worse prognosis in sepsis patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 May;35(5):e23753. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23753. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33704828 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of serum JKAP in acute ischemic stroke patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24270. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24270. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35274367 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

