How reliable is BMI? Bioimpedance analysis of body composition in underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese women
- PMID: 33083960
- PMCID: PMC8302488
- DOI: 10.1007/s11845-020-02403-3
How reliable is BMI? Bioimpedance analysis of body composition in underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese women
Abstract
Background: The human body consists of water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and minerals that build cells, tissues, and organs. In healthy people, the content of these molecules remains nearly constant. The body mass index (BMI) is commonly used to classify abnormal body composition among adults. According to the WHO, a high BMI is a major risk factor for many diseases. Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a commonly used method for assessing body composition in clinical practice and medical research.
Aims: The aim of this study was to identify the advantages and disadvantages of using BMI in diagnosis of underweight, overweight, and obesity, by comparing the value of the index with the values of body composition analysis parameters.
Methods: A total of 267 healthy women 18 to 35 years of age participated in this study. Bioelectrical impedance analysis was performed on all participants at the beginning of the experiment with an InBodyS10 device.
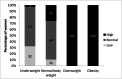
Results: In the BMI categories of overweight and obese, only women with excessive BFM were measured with BIA. The BMI category of normal body weight, apart from women with normal body composition, includes people with both deficient and excess body components, e.g., body fat or lean body mass. The BMI category of underweight includes women with different body compositions as well as people with excessive fat content.
Conclusions: The BMI is useful to provide a warning of excessive fat content in overweight and obese women, whereas among normal weight and underweight women, it may mask various types of body composition defects.
Keywords: BMI; Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA); Body composition.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison between bioelectrical impedance analysis and body mass index methods in determination of obesity prevalence in Ahvazi women.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007 Apr;61(4):478-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602545. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17063145
-
[Change of total body water dependent on age and nutritional status].Orv Hetil. 2024 Oct 27;165(43):1694-1699. doi: 10.1556/650.2024.33149. Print 2024 Oct 27. Orv Hetil. 2024. PMID: 39462290 Hungarian.
-
Combine body mass index and body fat percentage measures to improve the accuracy of obesity screening in young adults.Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017 Jan-Feb;11(1):11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 26944683
-
Beyond BMI: Conceptual Issues Related to Overweight and Obese Patients.Obes Facts. 2016;9(3):193-205. doi: 10.1159/000445380. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Obes Facts. 2016. PMID: 27286962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioelectrical impedance and lung function-associations with gender and central obesity: results of the EpiHealth study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jul 4;24(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03128-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38965493 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Body Fat and Organic Acid Anions Production Are Associated with Larger Kidney Size in ADPKD.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jan 19;58(2):152. doi: 10.3390/medicina58020152. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35208476 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and Inflammatory Biomarkers Predicting Sarcopenic Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk in Arab Women: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 13;26(12):5699. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125699. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565161 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Evaluation of a Nomogram to Predict Gallstone Disease Based on Body Composition.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 2;15:5947-5956. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S367642. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35811775 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle mass and chronic dizziness: a cross-sectional study of a Korean population.J Neurol. 2024 Mar;271(3):1213-1223. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12014-4. Epub 2023 Nov 1. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37910251
References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015–2020 2015 Dietary Guidelines for Americans 8th Edition. https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/. Accessed 3 Jan 2020
-
- Rzońca E, Bień A, Iwanowicz-Palus G. Eating disorders – an ongoing problem. J Educ Health Sport. 2016;6(12):267–273. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.198734. - DOI
-
- Bolanowski M, Zadrożna-Śliwka B, Zatońska K. Body composition studies — methods and possible application in hormonal disorders. Endocrinol Obes. 2005;1(1):20–25.
-
- World Health Organisation (2016) Obesity and overweight. Geneva: WHO Media Center
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical