Ultrastructural localization of glutamate delta 1 (GluD1) receptor immunoreactivity in the mouse and monkey striatum
- PMID: 33084025
- PMCID: PMC7987732
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.25051
Ultrastructural localization of glutamate delta 1 (GluD1) receptor immunoreactivity in the mouse and monkey striatum
Abstract
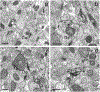
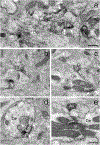
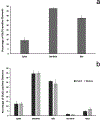
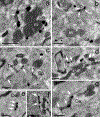
The glutamate receptor delta 1 (GluD1) is strongly expressed in the striatum. Knockout of GluD1 expression in striatal neurons elicits cognitive deficits and disrupts the thalamostriatal system in mice. To understand the potential role of GluD1 in the primate striatum, we compared the cellular and subcellular localization of striatal GluD1 immunoreactivity (GluD1-IR) in mice and monkeys. In both species, striatal GluD1-IR displayed a patchy pattern of distribution in register with the striosome/matrix compartmentation, but in an opposite fashion. While GluD1 was more heavily expressed in the striosomes than the matrix in the monkey caudate nucleus, the opposite was found in the mouse striatum. At the electron microscopic level, GluD1-IR was preferentially expressed in dendritic shafts (47.9 ± 1.2%), followed by glia (37.7 ± 2.5%), and dendritic spines (14.3 ± 2.6%) in the matrix of the mouse striatum. This pattern was not statistically different from the labeling in the striosome and matrix compartments of the monkey caudate nucleus, with the exception of a small amount of GluD1-positive unmyelinated axons and axon terminals in the primate striatum. Immunogold staining revealed synaptic and perisynaptic GluD1 labeling at putative axo-dendritic and axo-spinous glutamatergic synapses, and intracellular labeling on the surface of mitochondria. Confocal microscopy showed that GluD1 is preferentially colocalized with thalamic over cortical terminals in both the striosome and matrix compartments. These data provide the anatomical substrate for a deeper understanding of GluD1 regulation of striatal glutamatergic synapses, but also suggest possible extrasynaptic, glial, and mitochondrial GluD1 functions.
Keywords: RRIDs-AB_2571757; AB_2314065; AB_2716850; AB_2571759; AB_2301751; AB_2315569; cerebellin; matrix; parafascicular; patch; striosome; thalamostriatal.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Benamer N, Marti F, Lujan R, Hepp R, Aubier TG, Dupin A. a. M., Frébourg G, Pons S, Maskos U, Faure P, Hay YA, Lambolez B, & Tricoire L (2018). GluD1, linked to schizophrenia, controls the burst firing of dopamine neurons. Molecular Psychiatry, 23(3), 691–700. 10.1038/mp.2017.137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berridge G, Menassa DA, Moloney T, Waters PJ, Welding I, Thomsen S, Zuberi S, Fischer R, Aricescu AR, Pike M, Dale RC, Kessler B, Vincent A, Lim M, Irani SR, & Lang B (2018). Glutamate receptor δ2 serum antibodies in pediatric opsoclonus myoclonus ataxia syndrome. Neurology, 91(8), e714–e723. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006035 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

