Structural Insights into the Recognition of Mono- and Diacetylated Histones by the ATAD2B Bromodomain
- PMID: 33084328
- PMCID: PMC7884259
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01178
Structural Insights into the Recognition of Mono- and Diacetylated Histones by the ATAD2B Bromodomain
Abstract
Bromodomains exhibit preferences for specific patterns of post-translational modifications on core and variant histone proteins. We examined the ligand specificity of the ATAD2B bromodomain and compared it to its closely related paralogue in ATAD2. We show that the ATAD2B bromodomain recognizes mono- and diacetyllysine modifications on histones H4 and H2A. A structure-function approach was used to identify key residues in the acetyllysine-binding pocket that dictate the molecular recognition process, and we examined the binding of an ATAD2 bromodomain inhibitor by ATAD2B. Our analysis demonstrated that critical contacts required for bromodomain inhibitor coordination are conserved between the ATAD2/B bromodomains, with many residues playing a dual role in acetyllysine recognition. We further characterized an alternative splice variant of ATAD2B that results in a loss of function. Our results outline the structural and functional features of the ATAD2B bromodomain and identify a novel mechanism regulating the interaction of the ATAD2B protein with chromatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): EpiCypher (M.R.M. and M.-C.K.) is a commercial developer of the dCypher peptide-binding platform used in this study.
Figures

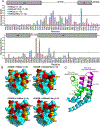
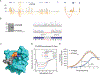

References
-
- Luger K; Richmond TJ The histone tails of the nucleosome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 1998, 8, 140–146. - PubMed
-
- Norton VG; Imai BS; Yau P; Bradbury EM Histone acetylation reduces nucleosome core particle linking number change. Cell 1989, 57, 449–457. - PubMed
-
- Li Y; Li Z; Dong L; Tang M; Zhang P; Zhang C; Cao Z; Zhu Q; Chen Y; Wang H; Wang T; Lv D; Wang L; Zhao Y; Yang Y; Wang H; Zhang H; Roeder RG; Zhu WG Histone H1 acetylation at lysine 85 regulates chromatin condensation and genome stability upon DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, 7716–7730. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 GM103449/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 GM116584/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 GM117683/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052040/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025062/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R15 GM104865/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA098993/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR028438/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR002781/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103399/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR008438/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023438/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

