Nutritive value and ruminal degradation of seven Chinese herbs as forage for Tan sheep
- PMID: 33084492
- PMCID: PMC8291884
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1834740
Nutritive value and ruminal degradation of seven Chinese herbs as forage for Tan sheep
Abstract
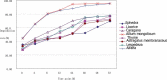
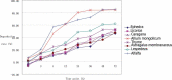
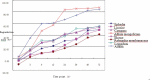
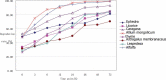
Tan sheep is an indigenous ovine breed of China known for its high meat quality and pleasing taste. Seven herbs of traditional Chinese medicine, namely, Ephedra sinica, Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Caragana korshinskii, Allium mongolicum, Thymus vulgaris, Astragalus membranaceus, and Lespedeza bicolor are commonly grazed by Tan sheep. It has been widely believed that these herbs are of high nutritive value, which may significantly contribute to the high meat quality and distinct flavor of Tan sheep. However, the nutritive values of these herbs have not been evaluated to date. In this study, samples of the seven herbs were collected from the steppe of Yanchi County of Ningxia Autonomous Region of China. The dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), ether extract (EE), ash (Ash), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), and acid detergent fiber (ADF) of these herbs were measured using locally cultivated alfalfa as the standard forage. Digestion of the dry matter, neutral detergent fiber, acid detergent fiber, and crude protein in the rumen of Tan sheep was examined using the nylon bag method, in order to evaluate their feeding nutritional value. Our results show that all the seven herbs meet the nutritional needs of ruminants based on the standard forage alfalfa. However, Ephedra, Glycyrrhiza, Caragana, Allium, Astragalus, and Lespedeza have higher nutritive value than Thymus (P < 0.05). According to the ruminal degradation rates of dry matter, neutral detergent fiber, acid detergent fiber, and crude protein, the nutritive value of Caragana, Allium, and Lespedeza is higher than that of Ephedra, Glycyrrhiza, Astragalus, and Thymus (P < 0.05). The overall nutritive value of Allium is the highest among the seven herbs and therefore Allium is recommended to better meet the nutritional needs of Tan sheep.
Keywords: Chinese herbs; Tan sheep; degradation; nutritive value.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li H, Ge CC, Feng F, et al. Fatty acids in longissimus dorsi from fattening Tan sheep, Small Fat-tail sheep and Tan Han hybrid sheep[J]. Food Res Develop. 2019;40(3):165–169.
-
- Hu YX.Development status and Countermeasures of Tan sheep industry in Yanchi County [J]. Modern Agric Sci Technol. 2017;30(12):261–263.
-
- Liu YN, Guo CH, Zhang ZF. Research progress in the application of Chinese herbal feed additives in the diet of pregnant and lactating ewes [J]. Chin J Herbivorous Animal Sci. 2018;38(1):57–59.
-
- Yang ZH. Multiple measures and pilot projects to accelerate the development of grass and animal husbandry[J]. Pratacultural Sci. 2015;32(8):1201–1205.
-
- Huang WY. Quality analysis of Tibetan sheep grazing on alpine meadow grassland in Qinghai Pastoral Area [J]. Meat Res. 2015;76(5):1212–1215.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
