Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration combined with either endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration or endoscopic ultrasound using the EBUS scope-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing and staging mediastinal diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33084766
- PMCID: PMC7536898
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1759
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration combined with either endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration or endoscopic ultrasound using the EBUS scope-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing and staging mediastinal diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Erratum for: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration combined with either endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration or endoscopic ultrasound using the EBUS scope-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing and staging mediastinal diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020 Nov 6;75:e1759err. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1759err. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 33174951 Free PMC article.
Abstract
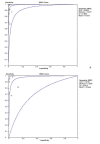
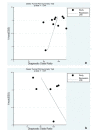
The present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the available evidence base on endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) combined with either endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) or endoscopic ultrasound using the EBUS scope-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-B-FNA) for diagnosing and staging mediastinal diseases. PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase were searched to identify suitable studies up to June 30, 2019. Two investigators independently reviewed articles and extracted relevant data. Data were pooled using random effect models to calculate diagnostic indices that included sensitivity and specificity. Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves were used to summarize the overall test performance. Data pooled from up to 16 eligible studies (including 10 studies of 963 patients about EBUS-TBNA with EUS-FNA and six studies of 815 patients with EUS-B-FNA) indicated that combining EBUS-TBNA with EUS-FNA was associated with slightly better diagnostic accuracy than combining it with EUS-B-FNA, in terms of sensitivity (0.87, 95%CI 0.83 to 0.90 vs. 0.84, 95%CI 0.80 to 0.88), specificity (1.00, 95%CI 0.99 to 1.00 vs. 0.96, 95%CI 0.93 to 0.97), diagnostic odds ratio (413.39, 95%CI 179.99 to 949.48 vs. 256.38, 95%CI 45.48 to 1445.32), and area under the SROC curve (0.99, 95%CI 0.97 to 1.00 vs. 0.97, 95%CI 0.92 to 1.00). The current evidence suggests that the combination of EBUS-TBNA with either EUS-FNA or EUS-B-FNA provides relatively high accuracy for diagnosing mediastinal diseases. The combination with EUS-FNA may be slightly better.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Vilmann P, Puri R. The complete “medical” mediastinoscopy (EUS-FNA + EBUS-TBNA) Minerva Med. 2007;98(4):331–8. - PubMed
-
- Dhooria S, Agarwal R, Aggarwal AN, Bal A, Gupta N, Gupta D. Differentiating tuberculosis from sarcoidosis by sonographic characteristics of lymph nodes on endobronchial ultrasonography: a study of 165 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148(2):662–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.01.028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

