Surgical results regarding the correction of macular hole with and without face-down posturing using 25% SF6 gas: a retrospective case series
- PMID: 33084811
- PMCID: PMC12289268
- DOI: 10.5935/0004-2749.20200044
Surgical results regarding the correction of macular hole with and without face-down posturing using 25% SF6 gas: a retrospective case series
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to compare the anatomical success rates of vitrectomy and SF6 gas tamponade for macular hole surgery with and without postoperative face-down posturing.
Methods: This was an observational, longitudinal, and retrospective case series analysis. The study included 52 eyes from 52 patients who underwent pars plana vitrectomy with trypan blue-assisted internal limiting membrane peeling and 25% SF6 tamponade for stages 2, 3, and 4 macular holes. After surgery, all patients were provided with a postoperative postural regimen: 31 patients were instructed not to maintain face-down posturing, whereas 21 were instructed to maintain face-down posturing for 7 days. The primary outcome measure was the macular hole closure rate. Statistical analysis was performed using Epi Info 7.1.
Results: A total of 47 (90.3%) patients achieved hole closure. The nonface-down posturing group and face-down posturing group obtained closure rates of 90.3% and 90.4%, respectively; these rates were not significantly different. Statistical analysis revealed that no significant differences existed in sex, age, hole duration, hole stage, preoperative visual acuity, or postoperative visual acuity between the two groups.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that macular hole surgery with the use of short duration gas (SF6) is safe and effective and that maintaining a postural orientation of nonface-down posturing is also safe. However, these recommendations should be assessed further in a prospective and randomized study to comprehensively delineate the associated benefits and risks.
Objetivos: Comparar as taxas de sucesso anatômico da vitrectomia e tamponamento de gás SF6 na cirurgia de buraco macular com e sem a postura pronada pós-operatória.
Métodos: Foi realizado um estudo observacional, longitudinal e retrospectivo de séries de casos. O estudo incluiu 52 olhos de 52 pacientes submetidos à vitrectomia posterior via pars-plana com peeling de membrana limitante interna auxiliada por azul trypan e tamponamento com gás SF6 a 25% para os estágios 2, 3 e 4 dos buracos maculares. Após a cirurgia, todos os pacientes foram orientados a manter um regime postural pós-operatório: 31 pacientes foram orientados a não realizar posição pronada de cabeça, enquanto 21 foram orientados a manter uma pronada pós-operatória por 7 dias. O objetivo principal foi a análise da taxa de fechamento do buraco macular. A análise estatística foi realizada usando Epi-Info 7.1.
Resultados: Um total de 47 (90,3%) pacientes obtiveram fechamento do buraco macular. O grupo de postura não pronada e o grupo de postura pronada obtiveram taxas de fechamento de 90,3%, e 90,4%, respectivamente; essas taxas não foram significativamente diferentes. A análise estatística revelou que não houve diferenças significativas relacionadas ao gênero, idade, duração do buraco macular, estágio do buraco macular, acuidade visual corrigida pré e pós-operatória entre os dois grupos.
Conclusão: Nossos resultados sugerem que a cirurgia para buraco macular com o uso de gás de curta duração (SF6) é segura e eficaz e que a manutenção de uma orientação pós-operatória de não-pronada também é segura. No entanto, essas recomendações devem ser avaliadas em um estudo prospectivo e randomizado para delinear de forma abrangente os riscos e benefícios associados.
Conflict of interest statement
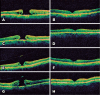
Figures
Similar articles
-
Face-down positioning or posturing after macular hole surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 21;11(11):CD008228. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008228.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37987517 Free PMC article.
-
Vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling versus vitrectomy with no peeling for idiopathic full-thickness macular hole (FTMH).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 5;(6):CD009306. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009306.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23740611
-
Intraocular Tamponade Choice with Vitrectomy and Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling for Idiopathic Macular Hole: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ophthalmol Retina. 2022 Jun;6(6):457-468. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2022.01.023. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Ophthalmol Retina. 2022. PMID: 35144020
-
Vitrectomy for idiopathic macular hole.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 12;2015(5):CD009080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009080.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25965055 Free PMC article.
-
Face-down positioning or posturing after macular hole surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;(12):CD008228. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008228.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 21;11:CD008228. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008228.pub3. PMID: 22161423 Updated.
Cited by
-
360-degree pedicled inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique without face-down posturing for large idiopathic macular holes: a retrospective case series.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2023 Oct 13;87(6):e20220252. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.2022-0252. eCollection 2023. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2023. PMID: 37851742 Free PMC article.
-
Pioneering evaluation in Brazil of microscope-integrated optical coherence tomography with a three-dimensional digital visualization system during pars plana vitrectomy for the treatment of macular hole.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025 May 19;11(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40942-025-00671-8. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025. PMID: 40383771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gass JD. Idiopathic senile macular holes: its early stages and pathogenesis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988;106(5):629–639. - PubMed
-
- Avila MP, Jalkh AE, Murakami K, Trempe CL, Schepens CL. Biomicroscopic study of the vitreous in macular breaks. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(11):1277–1283. - PubMed
-
- Kelly NE, Wendel RT. Vitreous surgery for idiopathic macular holes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991;109(5):654–659. Comment in: Arch Ophthalmol. 1991;109(5):654-9. - PubMed
-
- Thompson JT, Smiddy WE, Glaser BM, Sjaarda RN, Flynn HW., Jr. Intraocular tamponade duration and success of macular hole surgery. Retina. 1996;16(5):373–382. Comment in: Retina. 1998;18(1):84-6; author reply 86-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

