Three versus five intravitreal aflibercept injections as the initial loading phase in the treatment of diabetic macular edema: one-year results
- PMID: 33084817
- PMCID: PMC12289263
- DOI: 10.5935/0004-2749.20200078
Three versus five intravitreal aflibercept injections as the initial loading phase in the treatment of diabetic macular edema: one-year results
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the efficacy of three initial monthly intravitreal aflibercept injections followed by pro re nata (3+PRN) dosing versus five initial monthly intravitreal aflibercept injections followed by pro re nata (5+PRN) dosing in patients with diabetic macular edema.
Methods: A total of 60 treatment-naïve patients with macular edema who underwent intravitreal aflibercept injections (2 mg/0.05 mL) with at least one year of follow-up were analyzed in this retrospective and comparative study. The patients were divided into two groups according to the number of intravitreal aflibercept injections administered in the loading phase. The 3+PRN group comprised 27 patients, whereas the 5+PRN group comprised 33 patients. The visual and anatomical outcomes were compared between the two groups at baseline and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
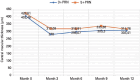
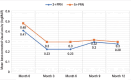
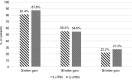
Results: Both 3+PRN and 5+PRN, showed statistically significant improvements in the best-corrected visual acuity and central macular thicknesse throughout the study period (p<0.001 and, p<0.001, respectively). There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of changes in the best-corrected visual acuity and central macular thickness (p=0.453 and, p=0.784, respectively). The mean number of intravitreal aflibercept injections was significantly greater in the 5+PRN group (6.1 ± 0.8) than in the 3+PRN group (3.9 ± 0.8) (p<0.001).
Conclusion: The 3+PRN and 5+PRN regimens showed similar 12-month visual and anatomical outcomes following treatment with intravitreal aflibercept injections in patients with macular edema.
Objetivo: Comparar a eficácia de três injeções intravítreas mensais iniciais de aflibercept, seguidas de dosagem de pro re nata (3+PRN) versus cinco injeções mensais iniciais intravítreas de aflibercept, seguidas de doses de pro re nata (5 + PRN) em pacientes com edema macular diabético.
Métodos: Foram analisados neste estudo retrospectivo e comparativo 60 pacientes que não receberam tratamento prévio com edema macular e foram submetidos a injeções intravítreas de aflibercept (2 mg/0,05 mL) com pelo menos um ano de acompanhamento. Os pacientes foram divididos em dois grupos de acordo com o número de injeções intravítreas de aflibercept administradas na fase inicial. O grupo 3+PRN compreendeu 27 pacientes, enquanto o grupo 5+PRN compreendeu 33 pacientes. Os resultados visuais e anatômicos foram comparados entre os dois grupos no período inicial e aos 3, 6, 9 e 12 meses.
Resultados: Tanto os grupos 3+PRN quanto 5+PRN mostraram melhoras estatisticamente significativas na acuidade visual melhor corrigida e na espessura macular central ao longo do período de estudo (p<0,001 e p <0,001, respectivamente). Não houve diferenças significativas entre os dois grupos em termos de alterações na acuidade visual melhor corrigida e na espessura macular central (p=0,453 e p=0,784, respectivamente). O número médio de injeções intravítreas de aflibercept foi significativamente maior no grupo 5+PRN (6,1 ± 0,8) do que no grupo 3+PRN (3,9 ± 0,8) (p <0,001).
Conclusão: Os regimes 3+PRN e 5+PRN mostraram resultados visuais e anatômicos semelhantes em 12 meses após o tratamento com injeções intravítreas de aflibercept em pacientes com edema macular.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Schmidt-Erfurth U, Garcia-Arumi J, Bandello F, Berg K, Chakravarthy U, Gerendas BS, et al. Guidelines for the management of diabetic macular edema by the European Society of Retina Specialists (EURETINA) Ophthalmologica. 2017;237(4):185–222. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. IV. Diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1984;91(12):1464–1474. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Bandello F, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Lang GE, Massin P, Schlingemann RO, Sutter F, Simader C, Burian G, Gerstner O, Weichselberger A, RESTORE study group The RESTORE study: ran ibizumab monotherapy or combined with laser versus laser mon otherapy for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(4):615–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical