Rationale and Design of the Genotype-Blinded Trial of Torasemide for the Treatment of Hypertension (BHF UMOD)
- PMID: 33084880
- PMCID: PMC7891239
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa166
Rationale and Design of the Genotype-Blinded Trial of Torasemide for the Treatment of Hypertension (BHF UMOD)
Abstract
Background: Genome-wide association studies have identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) near the uromodulin gene (UMOD) affecting uromodulin excretion and blood pressure (BP). Uromodulin is almost exclusively expressed in the thick ascending limb (TAL) of the loop of Henle and its effect on BP appears to be mediated via the TAL sodium transporter, NKCC2. Loop-diuretics block NKCC2 but are not commonly used in hypertension management. Volume overload is one of the primary drivers for uncontrolled hypertension, so targeting loop-diuretics to individuals who are more likely to respond to this drug class, using the UMOD genotype, could be an efficient precision medicine strategy.
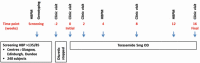
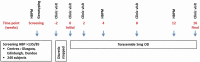
Methods: The BHF UMOD Trial is a genotype-blinded, multicenter trial comparing BP response to torasemide between individuals possessing the AA genotype of the SNP rs13333226 and those possessing the G allele. 240 participants (≥18 years) with uncontrolled BP, on ≥1 antihypertensive agent for ≥3 months, will receive treatment with Torasemide, 5 mg daily for 16 weeks. Uncontrolled BP is average home systolic BP (SBP) >135 mmHg and/or diastolic BP >85 mmHg. The primary outcome is the change in 24-hour ambulatory SBP area under the curve between baseline and end of treatment. Sample size was calculated to detect a 4 mmHg difference between groups at 90% power. Approval by West of Scotland Research Ethics Committee 5 (16/WS/0160).
Results: The study should conclude August 2021.
Conclusions: If our hypothesis is confirmed, a genotype-based treatment strategy for loop diuretics would help reduce the burden of uncontrolled hypertension.
Clinical trials registration: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03354897.
Keywords: NKCC2; blood pressure; furosemide; hypertension; loop-diuretic; uromodulin.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UMOD Genotype-Blinded Trial of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Response to Torasemide.Hypertension. 2024 Oct;81(10):2049-2059. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.23122. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 39077768 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of blood pressure extremes identifies variant near UMOD associated with hypertension.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 28;6(10):e1001177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001177. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21082022 Free PMC article.
-
Tamm-Horsfall protein/uromodulin deficiency elicits tubular compensatory responses leading to hypertension and hyperuricemia.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):F1062-F1076. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00233.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29357410 Free PMC article.
-
Torasemide prolonged release.Drugs. 2009 Jul 9;69(10):1363-72. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969100-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19583454 Review.
-
Uromodulin: from monogenic to multifactorial diseases.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015 Aug;30(8):1250-6. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfu300. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25228753 Review.
Cited by
-
Uromodulin biology.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Jun 28;39(7):1073-1087. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae008. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38211973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Uromodulin in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension.Hypertension. 2022 Nov;79(11):2419-2429. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19888. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 36378920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving Concepts in Uromodulin Biology, Physiology, and Its Role in Disease: a Tale of Two Forms.Hypertension. 2022 Nov;79(11):2409-2418. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.18567. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 35959659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UMOD Genotype-Blinded Trial of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Response to Torasemide.Hypertension. 2024 Oct;81(10):2049-2059. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.23122. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 39077768 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of metoprolol combined with torasemide in elderly patients with degenerative valvular heart disease and heart failure and its influence on NT-proBNP levels.Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Jul-Aug;39(4):945-949. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.4.7465. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37492298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, Hamburger RJ, Fye C, Lakshman R, Gottdiener J. Single-drug therapy for hypertension in men. A comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. The Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:914–921. - PubMed
-
- Iniesta R, Campbell D, Venturini C, Faconti L, Singh S, Irvin MR, Cooper-DeHoff RM, Johnson JA, Turner ST, Arnett DK, Weale ME, Warren H, Munroe PB, Cruickshank K, Padmanabhan S, Lewis C, Chowienczyk P. Gene variants at loci related to blood pressure account for variation in response to antihypertensive drugs between black and white individuals. Hypertension 2019; 74:614–622. - PubMed
-
- Padmanabhan S, Graham L, Ferreri NR, Graham D, McBride M, Dominiczak AF. Uromodulin, an emerging novel pathway for blood pressure regulation and hypertension. Hypertension 2014; 64:918–923. - PubMed
-
- Padmanabhan S, Melander O, Johnson T, Di Blasio AM, Lee WK, Gentilini D, Hastie CE, Menni C, Monti MC, Delles C, Laing S, Corso B, Navis G, Kwakernaak AJ, van der Harst P, Bochud M, Maillard M, Burnier M, Hedner T, Kjeldsen S, Wahlstrand B, Sjögren M, Fava C, Montagnana M, Danese E, Torffvit O, Hedblad B, Snieder H, Connell JM, Brown M, Samani NJ, Farrall M, Cesana G, Mancia G, Signorini S, Grassi G, Eyheramendy S, Wichmann HE, Laan M, Strachan DP, Sever P, Shields DC, Stanton A, Vollenweider P, Teumer A, Völzke H, Rettig R, Newton-Cheh C, Arora P, Zhang F, Soranzo N, Spector TD, Lucas G, Kathiresan S, Siscovick DS, Luan J, Loos RJ, Wareham NJ, Penninx BW, Nolte IM, McBride M, Miller WH, Nicklin SA, Baker AH, Graham D, McDonald RA, Pell JP, Sattar N, Welsh P, Munroe P, Caulfield MJ, Zanchetti A, Dominiczak AF; Global BPgen Consortium Genome-wide association study of blood pressure extremes identifies variant near UMOD associated with hypertension. PLoS Genet 2010; 6:e1001177. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous