Mitochondrial microRNA (MitomiRs) in cancer and complex mitochondrial diseases: current status and future perspectives
- PMID: 33084945
- PMCID: PMC11072739
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03670-0
Mitochondrial microRNA (MitomiRs) in cancer and complex mitochondrial diseases: current status and future perspectives
Abstract
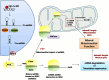
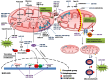
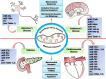
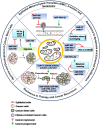
Mitochondria are not only important for cellular bioenergetics but also lie at the heart of critical metabolic pathways. They can rapidly adjust themselves in response to changing conditions and the metabolic needs of the cell. Mitochondrial involvement as well as its dysfunction has been found to be associated with variety of pathological processes and diseases. mitomiRs are class of miRNA(s) that regulate mitochondrial gene expression and function. This review sheds light on the role of mitomiRs in regulating different biological processes-mitochondrial dynamics, oxidative stress, cell metabolism, chemoresistance, apoptosis,and their relevance in metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. Insilico analysis of predicted targets of mitomiRs targeting energy metabolism identified several significantly altered pathways (needs in vivo validations) that may provide a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of human diseases. Last part of the review discusses about the clinical aspects of miRNA(s) and mitomiRs in Medicine.
Keywords: Cancer; Cardiovascular disease; Clinical medicine; Diabetes; Metabolic disorders; Neurodegenerative disorders; microRNA; mitomiR.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Emerging Role of MitomiRs in the Pathophysiology of Human Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:123-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663182
-
Mitochondrial MiRNA in Cardiovascular Function and Disease.Cells. 2019 Nov 21;8(12):1475. doi: 10.3390/cells8121475. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the roles and regulation of mitochondrial microRNAs (MitomiRs) in neurodegenerative diseases: Current status and advances.Mech Ageing Dev. 2023 Jul;213:111838. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2023.111838. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Mech Ageing Dev. 2023. PMID: 37329989 Review.
-
Deciphering the role of MitomiRs in cancer: A comprehensive review.Mitochondrion. 2023 May;70:118-130. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Mitochondrion. 2023. PMID: 37120081 Review.
-
MitomiRs in human inflamm-aging: a hypothesis involving miR-181a, miR-34a and miR-146a.Exp Gerontol. 2014 Aug;56:154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Exp Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 24607549 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune system cells from COVID-19 patients display compromised mitochondrial-nuclear expression co-regulation and rewiring toward glycolysis.iScience. 2021 Dec 17;24(12):103471. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103471. Epub 2021 Nov 18. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34812416 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs Action and Impact on Mitochondria Function, Metabolic Reprogramming and Chemoresistance of Cancer Cells: A Systematic Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 24;11(3):693. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030693. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial microRNAs: A Putative Role in Tissue Regeneration.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;9(12):486. doi: 10.3390/biology9120486. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer: mechanisms of resistance and future clinical interventions.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Aug 9;11(1):375. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02670-y. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40783392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-based coronal nanostructures for targeted mitochondria single molecule imaging.Chem Sci. 2022 Sep 10;13(38):11433-11441. doi: 10.1039/d2sc03329a. eCollection 2022 Oct 5. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36320584 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

