Age-related susceptibility to coronavirus infections: role of impaired and dysregulated host immunity
- PMID: 33085654
- PMCID: PMC7685716
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI144115
Age-related susceptibility to coronavirus infections: role of impaired and dysregulated host immunity
Abstract
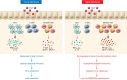
Human coronaviruses (hCoVs) cause severe respiratory illness in the elderly. Age-related impairments in innate immunity and suboptimal virus-specific T cell and antibody responses are believed to cause severe disease upon respiratory virus infections. This phenomenon has recently received increased attention, as elderly patients are at substantially elevated risk for severe COVID-19 disease and experience increased rates of mortality following SARS-CoV-2 infection compared with younger populations. However, the basis for age-related fatal pneumonia following pathogenic hCoVs is not well understood. In this Review, we provide an overview of our current understanding of hCoV-induced fatal pneumonia in the elderly. We describe host immune response to hCoV infections derived from studies of young and aged animal models and discuss the potential role of age-associated increases in sterile inflammation (inflammaging) and virus-induced dysregulated inflammation in causing age-related severe disease. We also highlight the existing gaps in our knowledge about virus replication and host immune responses to hCoV infection in young and aged individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- McIntosh K. Coronaviruses: a comparative review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;63(6–7):85–129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

