Effect of renal function on neutrophil decreases following eribulin administration
- PMID: 33085846
- PMCID: PMC7941480
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1258
Effect of renal function on neutrophil decreases following eribulin administration
Abstract
Background: Eribulin therapy has recently attracted attention from various viewpoints, including quality of life, and is considered a standard therapy for inoperable or recurrent breast cancer. Although a reduction in renal function reportedly decreases total eribulin clearance, its association with dose-limiting toxicity and the reduction of neutrophils remain unclear.
Aim: This study was aimed at analyzing the association between decreased renal function prior to eribulin administration and the occurrence of neutrophil reduction and time to treatment failure in patients with breast cancer.
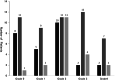
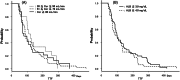
Methods and results: We retrospectively assessed patients with breast cancer, who underwent eribulin therapy between July 2011 and March 2018. Multivariate analysis revealed creatinine clearance <70 mL/min and serum albumin levels <3.9 mg/dL as predictive factors for neutrophil reduction. Even on increasing the relative dose intensity by these factors, no difference in time to treatment failure was observed, suggesting that treatment efficacy is potentially unaffected.
Conclusions: For continuous eribulin therapy, eribulin may need to be administered to individual patients in accordance with renal function and albumin levels before treatment initiation.
Keywords: breast cancer; eribulin; renal function; serum albumin levels; time to treatment failure.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Balixafortide plus eribulin in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: a phase 1, single-arm, dose-escalation trial.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jun;19(6):812-824. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30147-5. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29706375 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II Study of Eribulin Mesylate Administered Biweekly in Patients With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2-negative Metastatic Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Apr;20(2):160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31980406 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimization of G-CSF dosing schedule in patients treated with eribulin: a modeling approach.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;89(2):197-208. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04395-y. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34997290
-
Advances in therapy: eribulin improves survival for metastatic breast cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2010 Nov;21(10):885-9. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32833ed62e. Anticancer Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20838209 Review.
-
Eribulin mesylate for the treatment of late-stage breast cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 Dec;12(18):2883-90. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.637490. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 22087618 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors for Eribulin-induced Severe Neutropenia in Patients With Recurrent Breast Cancer.In Vivo. 2024 Jan-Feb;38(1):500-505. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13466. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38148090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Budrow J, et al. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activities of synthetic macrocyclic ketone analogs of halichondrin B. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1013‐1021. - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, O'Shaughnessy J, Loesch D, et al. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician's choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): a phase 3 open‐label randomized study. Lancet. 2011;377:914‐923. - PubMed
-
- Perez EA, Vogel CL, Irwin DH, Kirshner JJ, Patel R. Multicenter phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel in women with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:4216‐4223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

