Traffic Crash Severity Prediction-A Synergy by Hybrid Principal Component Analysis and Machine Learning Models
- PMID: 33086567
- PMCID: PMC7589286
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17207598
Traffic Crash Severity Prediction-A Synergy by Hybrid Principal Component Analysis and Machine Learning Models
Abstract
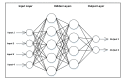
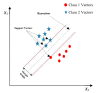
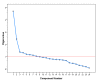
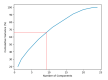
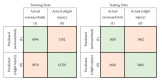
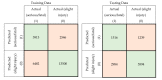
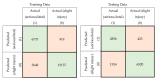
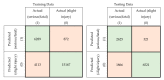
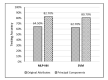
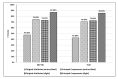
The accurate prediction of road traffic crash (RTC) severity contributes to generating crucial information, which can be used to adopt appropriate measures to reduce the aftermath of crashes. This study aims to develop a hybrid system using principal component analysis (PCA) with multilayer perceptron neural networks (MLP-NN) and support vector machines (SVM) in predicting RTC severity. PCA shows that the first nine components have an eigenvalue greater than one. The cumulative variance percentage explained by these principal components was found to be 67%. The prediction accuracies of the models developed using the original attributes were compared with those of the models developed using principal components. It was found that the testing accuracies of MLP-NN and SVM increased from 64.50% and 62.70% to 82.70% and 80.70%, respectively, after using principal components. The proposed models would be beneficial to trauma centers in predicting crash severity with high accuracy so that they would be able to prepare for appropriate and prompt medical treatment.
Keywords: emergency management; neural networks (NN); principal component analysis (PCA); support vector machine (SVM); traffic crash severity; vehicle crashes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peden M., Scurfield R., Sleet D., Hyder A.A., Mathers C., Jarawan E., Hyder A.A., Mohan D., Jarawan E. World Report on Road Traffic Injury Prevention. World Health Organizatio; Geneva, Switzerland: 2004.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on Road Safety. World Health Organizatio; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018.
-
- Mujalli R.O., de Oña J. Injury severity models for motor vehicle accidents: A review. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2013;166:255–270. doi: 10.1680/tran.11.00026. - DOI
-
- Sanguansat P. Principal Component Analysis: Engineering Applications. BoD–Books on Demand, Intech; Rijeka, Croatia: 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

