Single-Dose Cisplatin Pre-Treatment Enhances Efficacy of ROBO1-Targeted Radioimmunotherapy
- PMID: 33086574
- PMCID: PMC7589062
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21207728
Single-Dose Cisplatin Pre-Treatment Enhances Efficacy of ROBO1-Targeted Radioimmunotherapy
Abstract
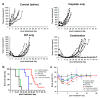
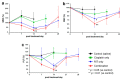
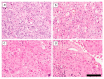
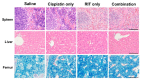
We previously reported that radioimmunotherapy (RIT) using 90Y-labeled anti-ROBO1 IgG (90Y-B5209B) achieved significant anti-tumor effects against small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) xenografts. However, subsequent tumor regrowth suggested the necessity for more effective therapy. Here, we evaluated the efficacy of combination 90Y-B5209B and cisplatin therapy in NCI-H69 SCLC xenograft mice. Mice were divided into four therapeutic groups: saline, cisplatin only, RIT only, or combination therapy. Either saline or cisplatin was administered by injection one day prior to the administration of either saline or 90Y-B5209B. Tumor volume, body weight, and blood cell counts were monitored. The pathological analysis was performed on day seven post injection of 90Y-B5209B. The survival duration of the combination therapy group was significantly longer than that of the group treated with RIT alone. No significant survival benefit was observed following the isolated administration of cisplatin (relative to saline). Pathological changes following combination therapy were more significant than those following the isolated administration of RIT. Although combination therapy was associated with an increase of several adverse effects such as weight loss and pancytopenia, these were transient. Thus, cisplatin pre-treatment can potentially enhance the efficacy of 90Y-B5209B, making it a promising therapeutic strategy for SCLC.
Keywords: ROBO1; cisplatin; combination therapy; radioimmunotherapy; small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib enhances the efficacy of 90 Y-labeled B5209B radioimmunotherapy targeting ROBO1 without increased toxicity in small-cell lung cancer xenograft mice.Nucl Med Commun. 2024 Jan 1;45(1):68-76. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001775. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Nucl Med Commun. 2024. PMID: 37728607 Free PMC article.
-
90Y-Labeled Anti-ROBO1 Monoclonal Antibody Exhibits Antitumor Activity against Small Cell Lung Cancer Xenografts.PLoS One. 2015 May 27;10(5):e0125468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125468. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26017283 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of c-kit-targeted radioimmunotherapy using 90Y-labeled anti-c-kit antibodies in a mouse model of small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059248. Epub 2013 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516616 Free PMC article.
-
Cilengitide targeting of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptor synergizes with radioimmunotherapy to increase efficacy and apoptosis in breast cancer xenografts.Cancer Res. 2002 Aug 1;62(15):4263-72. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12154028
-
Combination Radioimmunotherapy Strategies for Solid Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 8;20(22):5579. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225579. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing reveals CK19 + cancer stem cells and their specific SPP1 + tumor-associated macrophage niche in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Int. 2024 Feb;18(1):73-90. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10615-9. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38159218
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib enhances the efficacy of 90 Y-labeled B5209B radioimmunotherapy targeting ROBO1 without increased toxicity in small-cell lung cancer xenograft mice.Nucl Med Commun. 2024 Jan 1;45(1):68-76. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001775. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Nucl Med Commun. 2024. PMID: 37728607 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP16K19809, JP18K15335, 18K07778, 17K10497, 18H02774, and 20K08148/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- P06009/New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization
- the Funding Program for World-Leading Innovative R&D on Science and Technology (FIRST Program)/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

