Expression of POU2F3 Transcription Factor Control Inflammation, Immunological Recruitment and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer in Mice
- PMID: 33086657
- PMCID: PMC7603360
- DOI: 10.3390/biology9100341
Expression of POU2F3 Transcription Factor Control Inflammation, Immunological Recruitment and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer in Mice
Abstract
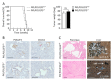
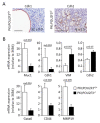
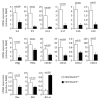
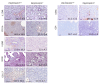
TUFT cells have been described as strong modulators of inflammatory cells in several tissues including pancreas. TUFT cells, also known as DCLK1+ cells, are dependent of the transcriptional factor POU2F3. Several works report DCLK1+ cells in early stages of PDAC development suggesting an important role of TUFT cells in PDAC development. Therefore, we developed a mice model (PDX1-Cre;KrasG12D;Ink4afl/fl), known as PKI model, deficient or not of POU2F3. In this animal model, deficiency of POU2F3 results in the absence of TUFT cells in PDAC as expected. Although, tumor development and growth are not significantly influenced, the development of liver metastasis was almost completely inhibited in POU2F3-deficient mice. Surprisingly, the absence of metastasis was associated with a higher expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers, but to a lower inflammatory microenvironment suggesting that inflammation influences metastasis production more than epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in this animal model. We can conclude that POU2F3 could be a new therapeutic target for control PDAC progression.
Keywords: PDAC; POU2F3; TUFT cells; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of POU2F3 Transcription Factor and POU2AF2, POU2F3 Coactivator, in Tuft Cell-like Carcinoma and Other Tumors.Am J Surg Pathol. 2025 Jan 1;49(1):62-72. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002313. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Am J Surg Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39319626
-
An exploratory study for tuft cells in the breast and their relevance in triple-negative breast cancer: the possible relationship of SOX9.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 13;23(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10949-5. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37179317 Free PMC article.
-
Lunatic Fringe is a potent tumor suppressor in Kras-initiated pancreatic cancer.Oncogene. 2016 May 12;35(19):2485-95. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.306. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26279302
-
The critical roles and therapeutic implications of tuft cells in cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 9;13:1047188. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1047188. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36569325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in tuft cells, a chemosensory cell in sequential diseases of the pancreas.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023 Jul;1878(4):188911. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188911. Epub 2023 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37182665 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory network analysis of Dclk1 gene expression reveals a tuft cell-ILC2 axis that inhibits pancreatic tumor progression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 12:2024.08.30.610508. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610508. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Jun 24;44(6):115734. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115734. PMID: 39257805 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Tuft cells transdifferentiate to neural-like progenitor cells in the progression of pancreatic cancer.Dev Cell. 2025 Mar 24;60(6):837-852.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.12.003. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39721583
-
Regulatory network analysis of Dclk1 gene expression reveals a tuft cell-ILC2 axis that inhibits pancreatic tumor progression.Cell Rep. 2025 Jun 24;44(6):115734. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115734. Epub 2025 May 22. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40408246 Free PMC article.
-
Tuft Cells: Context- and Tissue-Specific Programming for a Conserved Cell Lineage.Annu Rev Pathol. 2023 Jan 24;18:311-335. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-042320-112212. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36351364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appearance of tuft cells during prostate cancer progression.Oncogene. 2023 Jul;42(31):2374-2385. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02743-1. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37386128 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

