Country Level Diversity of the HIV-1 Pandemic between 1990 and 2015
- PMID: 33087461
- PMCID: PMC7944450
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01580-20
Country Level Diversity of the HIV-1 Pandemic between 1990 and 2015
Abstract
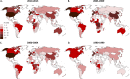
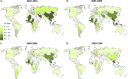
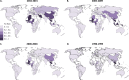
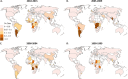
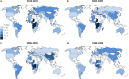
The global diversity of HIV forms a major challenge to the development of an HIV vaccine, as well as diagnostic, drug resistance, and viral load assays, which are essential to reaching the UNAIDS 90:90:90 targets. We sought to determine country level HIV-1 diversity globally between 1990 and 2015. We assembled a global HIV-1 molecular epidemiology database through a systematic literature search and a global survey. We searched PubMed, EMBASE (Ovid), CINAHL (Ebscohost), and Global Health (Ovid) for HIV-1 subtyping studies published from 1 January 1990 to 31 December 2015. We collected additional unpublished data through a global survey of experts. Prevalence studies with original HIV-1 subtyping data collected between 1990 and 2015 were included. This resulted in a database with 383,519 subtyped HIV-1 samples from 116 countries over four time periods (1990 to 1999, 2000 to 2004, 2005 to 2009, and 2010 to 2015). We analyzed country-specific numbers of distinct HIV-1 subtypes, circulating recombinant forms (CRFs), and unique recombinant forms (URFs) in each time period. We also analyzed country-specific proportions of infections due to HIV-1 recombinants, CRFs, and URFs and calculated the Shannon diversity index for each country. Finally, we analyzed global temporal trends in each of these measures of HIV-1 diversity. We found extremely wide variation in complexity of country level HIV diversity around the world. Central African countries such as Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, and Republic of the Congo have the most diverse HIV epidemics. The number of distinct HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants was greatest in Western Europe (Spain and France) and North America (United States) (up to 39 distinct HIV-1 variants in Spain). The proportion of HIV-1 infections due to recombinants was highest in Southeast Asia (>95% of infections in Viet Nam, Cambodia, and Thailand), China, and West and Central Africa, mainly due to high proportions of CRF01_AE and CRF02_AG. Other CRFs played major roles (>75% of HIV-1 infections) in Estonia (CRF06_cpx), Iran (CRF35_AD), and Algeria (CRF06_cpx). The highest proportions of URFs (>30%) were found in Myanmar, Republic of the Congo, and Argentina. Global temporal analysis showed consistent increases over time in country level numbers of distinct HIV-1 variants and proportions of CRFs and URFs, leading to increases in country level HIV-1 diversity. Our study provides epidemiological evidence that the HIV pandemic is diversifying at country level and highlights the increasing challenge to prevention and treatment efforts. HIV-1 molecular epidemiological surveillance needs to be continued and improved.IMPORTANCE This is the first study to analyze global country level HIV-1 diversity from 1990 to 2015. We found extremely wide variation in complexity of country level HIV diversity around the world. Central African countries have the most diverse HIV epidemics. The number of distinct HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants was greatest in Western Europe and North America. The proportion of HIV-1 infections due to recombinants was highest in South-East Asia, China, and West and Central Africa. The highest proportions of URFs were found in Myanmar, Republic of the Congo, and Argentina. Our study provides epidemiological evidence that the HIV pandemic is diversifying at country level and highlights the increasing challenge to HIV vaccine development and diagnostic, drug resistance, and viral load assays.
Keywords: CRF; HIV; URF; circulating recombinant form; diversity; molecular epidemiology; recombinant; unique recombinant form.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. 2020. Global AIDS update. UNAIDS, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- United Nations. 2015. Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. United Nations, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

