Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Friend or Foe?
- PMID: 33087588
- PMCID: PMC8283292
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl20223
Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Friend or Foe?
Abstract
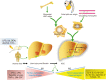
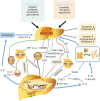
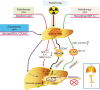
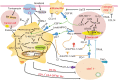
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, and it has diverse etiologies with multiple mechanisms. The diagnosis of HCC typically occurs at advanced stages when there are limited therapeutic options. Hepatocarcinogenesis is considered a multistep process, and hepatic macrophages play a critical role in the inflammatory process leading to HCC. Emerging evidence has shown that tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are crucial components defining the HCC immune microenvironment and represent an appealing option for disrupting the formation and development of HCC. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the polarization and function of TAMs in the pathogenesis of HCC, as well as the mechanisms underlying TAM-related anti-HCC therapies. Eventually, novel insights into these important aspects of TAMs and their roles in the HCC microenvironment might lead to promising TAM-focused therapeutic strategies for HCC.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Epigenetic modification; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Macrophage polarization; Tumor-associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting tumor associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 May;199:114990. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.114990. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35288152 Review.
-
Macrophages as Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Jun 4;23(6):780-790. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0660. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38310642 Review.
-
Role of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: impact, mechanism, and therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1429812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429812. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic tuning of tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs): a potential approach in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immunotherapy.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Sep 25;26:e18. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.9. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39320855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor‑associated macrophages activated in the tumor environment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Characterization and treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Oct;65(4):100. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5688. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39239752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and neighboring cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2022 Jul;28(3):333-350. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0308. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34665953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A risk scoring model based on M2 macrophage-related genes for predicting prognosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 May 20;44(5):827-840. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.04. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38862440 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Advances in immunotherapy for hepatitis B virus associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients.World J Hepatol. 2024 Oct 27;16(10):1158-1168. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i10.1158. World J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39474576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 on Immune Cells Is Related to a Better Prognosis in Biliary Tract Cancer.Gut Liver. 2023 Nov 15;17(6):933-941. doi: 10.5009/gnl220206. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Gut Liver. 2023. PMID: 36510775 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Stellate Cell Modulates the Immune Microenvironment in the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 15;23(18):10777. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810777. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142683 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

