A combined fMRI and EMG study of emotional contagion following partial sleep deprivation in young and older humans
- PMID: 33087746
- PMCID: PMC7578048
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74489-9
A combined fMRI and EMG study of emotional contagion following partial sleep deprivation in young and older humans
Abstract
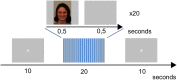
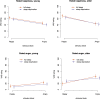
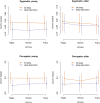
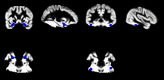
Sleep deprivation is proposed to inhibit top-down-control in emotion processing, but it is unclear whether sleep deprivation affects emotional mimicry and contagion. Here, we aimed to investigate effects of partial sleep deprivation on emotional contagion and mimicry in young and older humans. Participants underwent partial sleep deprivation (3 h sleep opportunity at the end of night), crossed-over with a full sleep condition in a balanced order, followed by a functional magnetic resonance imaging and electromyography (EMG) experiment with viewing of emotional and neutral faces and ratings of emotional responses. The final sample for main analyses was n = 69 (n = 36 aged 20-30 years, n = 33 aged 65-75 years). Partial sleep deprivation caused decreased activation in fusiform gyri for angry faces and decreased ratings of happiness for all stimuli, but no significant effect on the amygdala. Older participants reported more anger compared to younger participants, but no age differences were seen in brain responses to emotional faces or sensitivity to partial sleep deprivation. No effect of the sleep manipulation was seen on EMG. In conclusion, emotional contagion, but not mimicry, was affected by sleep deprivation. Our results are consistent with the previously reported increased negativity bias after insufficient sleep.The Stockholm sleepy brain study: effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive and emotional processing in young and old. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02000076 .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased sleep duration is associated with increased fMRI responses to emotional faces in children.Neuropsychologia. 2016 Apr;84:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.01.028. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Neuropsychologia. 2016. PMID: 26821063
-
Sleep deprivation and interference by emotional distracters.Sleep. 2010 Oct;33(10):1305-13. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.10.1305. Sleep. 2010. PMID: 21061852 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sleep loss on emotion recognition: a dissociation between face and word stimuli.Exp Brain Res. 2014 Oct;232(10):3147-57. doi: 10.1007/s00221-014-3995-9. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Exp Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24913142
-
Effects of sleep deprivation on cognition.Prog Brain Res. 2010;185:105-29. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53702-7.00007-5. Prog Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 21075236 Review.
-
Sleep loss and emotion: A systematic review and meta-analysis of over 50 years of experimental research.Psychol Bull. 2024 Apr;150(4):440-463. doi: 10.1037/bul0000410. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Psychol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38127505
Cited by
-
Elucidating the Effects of Sleep Deprivation: Exploring fMRI Imaging Biomarkers to Analyze Brain Functions Related to Insomnia.Adv Biomed Res. 2024 Dec 28;13:125. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_466_23. eCollection 2024. Adv Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 40007726 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Specific Functional Connectivity Changes After Partial Sleep Deprivation Are Correlated With Neurocognitive and Molecular Signatures.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70272. doi: 10.1111/cns.70272. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39932149 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sleep deprivation on language-related brain functional connectivity: differences by gender and age.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2024 Jun;24(3):517-526. doi: 10.3758/s13415-024-01161-4. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38273105
-
Which emotion regulation strategy is efficient for whom? Reappraisal and suppression efficiency for adaptive and maladaptive personality profiles.J Pers. 2025 Apr;93(2):463-488. doi: 10.1111/jopy.12948. Epub 2024 May 27. J Pers. 2025. PMID: 38801169 Free PMC article.
-
Should perception of emotions be classified according to threat detection rather than emotional valence? An updated meta-analysis for a whole-brain atlas of emotional faces processing.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023 Oct 19;48(5):E376-E389. doi: 10.1503/jpn.230065. Print 2023 Sep-Oct. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37857413 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

