Post-translational modification of KRAS: potential targets for cancer therapy
- PMID: 33087838
- PMCID: PMC8285426
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-00542-y
Post-translational modification of KRAS: potential targets for cancer therapy
Abstract
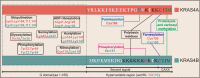
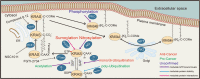
Aberrant activation of the RAS superfamily is one of the critical factors in carcinogenesis. Among them, KRAS is the most frequently mutated one which has inspired extensive studies for developing approaches to intervention. Although the cognition toward KRAS remains far from complete, mounting evidence suggests that a variety of post-translational modifications regulate its activation and localization. In this review, we summarize the regulatory mode of post-translational modifications on KRAS including prenylation, post-prenylation, palmitoylation, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, SUMOylation, acetylation, nitrosylation, etc. We also highlight the recent studies targeting these modifications having exhibited potent anti-tumor activities.
Keywords: KRAS; SUMOylation; acetylation; cancer therapy; nitrosylation; oncogene; palmitoylation; phosphorylation; post-translational modification; postprenylation; prenylation; ubiquitination.
© 2020. CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

