SPATA33 is an autophagy mediator for cargo selectivity in germline mitophagy
- PMID: 33087875
- PMCID: PMC7937689
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-020-00638-2
SPATA33 is an autophagy mediator for cargo selectivity in germline mitophagy
Abstract
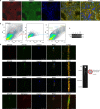
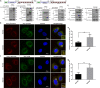
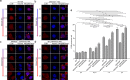
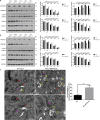
Selective autophagic degradation of mitochondria (mitophagy) is important in maintaining proper cellular homeostasis. Here, we found that SPATA33 is a novel autophagy mediator for mitophagy in testis. The SPATA33 protein localizes on mitochondria via its binding of the carboxyl terminal with the outer mitochondrial membrane protein VDAC2. Upon starvation induction, SPATA33 is recruited to autophagosome by binding the autophagy machinery ATG16L1 via its N-terminal along with mitochondria. Notably, Spata33 knockout inhibited autophagy and overexpression can promote autophagosome formation for mitochondrial sequestration. Therefore, SPATA33 confers selectivity for mitochondrial degradation and promotes mitophagy in male germline cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
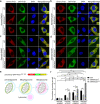
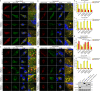
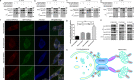
Comment in
-
SPATA33 functions as a mitophagy receptor in mammalian germline.Autophagy. 2021 May;17(5):1284-1286. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1909836. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33818286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hermo L, Pelletier RM, Cyr DG, Smith CE. Surfing the wave, cycle, life history, and genes/proteins expressed by testicular germ cells. Part 1: background to spermatogenesis, spermatogonia, and spermatocytes. Microsc Res Tech. 2010;73:241–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

