Melanoma recurrence patterns and management after adjuvant targeted therapy: a multicentre analysis
- PMID: 33087895
- PMCID: PMC7851118
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-01121-y
Melanoma recurrence patterns and management after adjuvant targeted therapy: a multicentre analysis
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant targeted therapy (TT) improves relapse free survival in patients with resected BRAF mutant stage III melanoma. The outcomes and optimal management of patients who relapse after adjuvant TT is unknown.
Methods: Patients from twenty-one centres with recurrent melanoma after adjuvant TT were included. Disease characteristics, adjuvant therapy, recurrence, treatment at relapse and outcomes were examined.
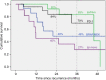
Results: Eighty-five patients developed recurrent melanoma; nineteen (22%) during adjuvant TT. Median time to first recurrence was 18 months and median follow-up from first recurrence was 31 months. Fifty-eight (68%) patients received immunotherapy (IT) or TT as 1st line systemic therapy at either first or subsequent recurrence and had disease that was assessable for response. Response to anti-PD-1 (±trial agent), combination ipilimumab-nivolumab, TT rechallenge and ipilimumab monotherapy was 63%, 62% 25% and 10% respectively. Twenty-eight (33%) patients had died at census, all from melanoma. Two-year OS was 84% for anti-PD-1 therapy (±trial agent), 92% for combination ipilimumab and nivolumab, 49% for TT and 45% for ipilimumab monotherapy (p = 0.028).
Conclusions: Patients who relapse after adjuvant TT respond well to subsequent anti-PD-1 based therapy and have outcomes similar to those seen when first line anti-PD-1 therapy is used in stage IV melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
P.B.: Travel support: MSD G.V.L.: Consultancy: Aduro, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mass-Array, Merck, MSD, Novartis, OncoSec Medical, Pierre Fabre, Roche, QBiotics, Skyline DX and Sandoz. A.M.M.: Consultancy: BMS, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Pierre-Fabre. Acknowledgement Cancer Institute NSW Fellowship and Melanoma Institute Australia. VA. Consultancy: BMS, MSD, Merck, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Roche, NEKTAR. Speaker honoraria: BMS, MSD, Merck, Novartis. Travel support: BMS, Oncosec. J.V.C.: Consultancy: Sanofi-Genzyme, BMS. R.J.S.: Consultancy: Asana Biosciences, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Merck, Lovance. Research funding: Merck, Amgen. M.N.: Consultancy: Novartis, BMS, Pierre-Fabre. Speaker honoraria: Novartis, BMS, Pierre-Fabre. K.K.: Personal fees: Amgen, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Novartis, Amgen, Pierre Fabre, Medac. A.H.: Consultancy: Amgen, BMS, MerckSerono, MSD/Merck, Philogen, Pierre Fabre, Provectus, Regeneron, Roche, OncoSec, Sanofi-Genzyme, Sun Pharma, Novartis Pharma, Almirall Hermal. Speaker honoraria: Amgen, BMS, MSD/Merck, Pierre Fabre, Provectus, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme Novartis Pharma. Research funding: Amgen, BMS, MerckSerono, MSD/Merck, Philogen, Pierre Fabre, Provectus, Regeneron Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Novartis Pharma. R.P.: Consultancy: Pierre Faber, Bayer, Octimet, Clovis Oncology, Novartis, Karus Therapeutics, Biosceptre, BMS, Cybrexa, Ellipses, CV6 Therapeutics, Astex Therapeutics, Sanofi Aventis. Speaker honoraria: AstraZeneca, Novartis, Bayer, Tesaro, BMS. Travel support: BMS, MSD. P.A.A.: Consultancy: Bristol Myers-Squibb, Roche-Genentech, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Array, Novartis, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, Incyte, NewLink Genetics, Genmab, Medimmune, AstraZeneca, Syndax, SunPharma, Sanofi, Idera, Ultimovacs, Sandoz, Immunocore, 4SC, Alkermes, Italfarmaco, Nektar, Boehringer-Ingelheim. Research funding: Bristol Myers-Squibb, Roche-Genentech, Array. Travel support: MSD. L.Z.: Consultancy: BMS, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Sunpharma, Sanofi, MSD. Honoraria from Roche, BMS, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre. Research funding: Novartis; Travel support: BMS, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Amgen, Novartis, Sunpharma. D.S.: Consultancy: BMS, Merck Serono, Amgen, Immunocore, Incyte, 4SC, Pierre Fabre, Mologen, Merck/MSD, Sanofi/Regeneron. Speaker honoraria: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, BMS, Merck Serono, Amgen, Immunocore, Incyte, 4SC, Pierre Fabre, Array BioPharma, InFlarX, Philogen, Regeneron, Merck/MSD, Sandoz/Hexal, Neracare. Research funding: Novartis, BMS. Travel support: Roche/Genentech, Novartis, BMS, Merck Serono, Amgen, Merck/MSD. C.A.: Travel support: Amgen, BMS, Roche. C.L.: Consultancy: Avantis Medical Systems, BMS, MSD, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Merck Serono, Sanofi. Research funding: BMS, Roche. Speaker honoraria: BMS, MSD, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Incyte. Travel support: BMS, MSD, CR: Consultancy: BMS, Pierre Fabre, Novartis, Merck, MSD, Roche, Sanofi, Biothera, Curevac. T.L.: Consultancy: MSD, Pierre Fabre, Novartis. S.P.: Speaker honoraria: Merck CUB: Consultancy: BMS, MSD, Roche, Novartis, GSK, AZ, Pfizer, Lilly, GenMab, Pierre Fabre, Third Rock Ventures. Research funding: BMS, Novartis, NanoString. Stockowner: Uniti Cars. A.K.: Speaker honoraria: Novartis. Travel support: Novartis. A.V.W.: Travel support: BMS, Novartis, MSD. M.S.C.: Consultancy: BMS, MSD, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Pierre Fabre, Nektar, Eisia, Sanofi, Merck Serono, Ideay, Q biotics. M.S.: Consultancy: BMS, Merch, MSD. Speaker honoraria: BMS, Merck, MSD. Research funding: BMS. Travel support: BMS, Merck, Roche. A.H.: Consultancy: Novartis, BMS, MSD, Pierre-Fabre. All remaining authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Larkin JMG, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob J-J, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. 5-year survival outcomes of the CheckMate 067 phase 3 trial of nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) combination therapy in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:1535–1546. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910836. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Long GV, Flaherty KT, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, Levchenko E, de Braud F, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib versus dabrafenib monotherapy in patients with metastatic BRAF V600E/K-mutant melanoma: long-term survival and safety analysis of a phase 3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:1631–1639. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx176. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grob JJ, Amonkar MM, Karaszewska B, Schachter J, Drummer R, Mackiewicz A, et al. Comparison of dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy with vemurafenib monotherapy on health-related quality of life in patients with unresectable or metastatic cutaneous BRAF Val600-mutation-positive melanoma (COMBI-v): results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1389–1398. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00087-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

