Next-generation GRAB sensors for monitoring dopaminergic activity in vivo
- PMID: 33087905
- PMCID: PMC7648260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-020-00981-9
Next-generation GRAB sensors for monitoring dopaminergic activity in vivo
Abstract
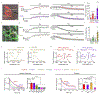
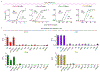
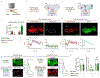
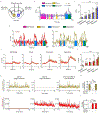
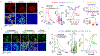
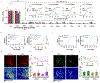
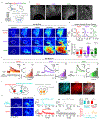
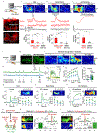
Dopamine (DA) plays a critical role in the brain, and the ability to directly measure dopaminergic activity is essential for understanding its physiological functions. We therefore developed red fluorescent G-protein-coupled receptor-activation-based DA (GRABDA) sensors and optimized versions of green fluorescent GRABDA sensors. In response to extracellular DA, both the red and green GRABDA sensors exhibit a large increase in fluorescence, with subcellular resolution, subsecond kinetics and nanomolar-to-submicromolar affinity. Moreover, the GRABDA sensors resolve evoked DA release in mouse brain slices, detect evoked compartmental DA release from a single neuron in live flies and report optogenetically elicited nigrostriatal DA release as well as mesoaccumbens dopaminergic activity during sexual behavior in freely behaving mice. Coexpressing red GRABDA with either green GRABDA or the calcium indicator GCaMP6s allows tracking of dopaminergic signaling and neuronal activity in distinct circuits in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
F.S. and Y. L. have filed patent applications whose value might be affected by this publication.
Figures








References
-
- Björklund A & Dunnett SB Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: an update. Trends in neurosciences 30, 194–202 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Wise RA Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nature reviews neuroscience 5, 483–494 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Tidey JW & Miczek KA Social defeat stress selectively alters mesocorticolimbic dopamine release: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain research 721, 140–149 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Robinson DL, Venton BJ, Heien ML & Wightman RM Detecting subsecond dopamine release with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry in vivo. Clinical chemistry 49, 1763–1773 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

