Analysis of flavor and taste attributes differences treated by chemical preservatives: a case study in strawberry fruits treated by 1-methylcyclopropene and chlorine dioxide
- PMID: 33087951
- PMCID: PMC7550547
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04474-7
Analysis of flavor and taste attributes differences treated by chemical preservatives: a case study in strawberry fruits treated by 1-methylcyclopropene and chlorine dioxide
Abstract
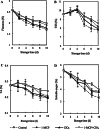
Flavor and taste attributes of fruits varied by different preservatives treatments. Changes in sugars, organic acids, amino acids as well as volatiles of strawberries treated with 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) and/or chlorine dioxide (ClO2) were evaluated during storage period in this study. Our results revealed that the decreases of tartaric acid, malic acid, citric acid, titratable acidity (TA), sucrose and soluble sugar contents were significantly inhibited by 1-MCP + ClO2. The fructose and glucose contents of all groups remained stable and slightly increased at the last period of 10 days. However, different treatments had no influence on content of succinic acid. Moreover, the highest sweet taste (77.37 mg 100 g-1 fresh weight) and lowest bitter taste (3.44 mg 100 g-1 fresh weight) free amino acids (FAA) were observed in the strawberries treated by 1-MCP combined with ClO2 treatment as compared to other treatments and control. (E)-2-hexenal was the most abundant volatile and showed a significant increase trend during strawberry storage. More interestingly, ethyl butyrate, fruit-like aroma, could be recovered in content by 1-MCP, ClO2 alone and their combination treatment. Compared with other treatments, the significant different flavor in ClO2 treatment was identified by principle component analysis. In addition, methyl hexanoate and 4-methoxy-2,5-dimethylfuran-3(2H)-one (DMMF) were the major factors that affected the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) of strawberries through the whole storage. Taken together, 1-MCP coupled with ClO2 could be a complex preservative to maintain strawberries quality by regulating the flavor and taste attributes.
Keywords: 1-MCP; ClO2; Flavor; Strawberry; Vocs.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abonyi BI, Feng H, Tang J, Edwards CG, Chew BP, Mattinson DS, Fellman JK. Quality retention in strawberry and carrot purees dried with Refractance WindowTM System. J Food Sci. 2002 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb09452.x. - DOI
-
- Caleb OJ, Wegner G, Rolleczek C, Herppich WB, Geyer M, Mahajan PV. Hot water dipping: impact on postharvest quality, individual sugars, and bioactive compounds during storage of “Sonata” strawberry. Sci Hortic. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.07.021. - DOI
-
- Chen Z, Zhu C. Combined effects of aqueous chlorine dioxide and ultrasonic treatments on postharvest storage quality of plum fruit (Prunus salicina L.) Postharvest Biol Technol. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2011.03.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
