Effects of different strains and fermentation method on nattokinase activity, biogenic amines, and sensory characteristics of natto
- PMID: 33087955
- PMCID: PMC7550479
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04478-3
Effects of different strains and fermentation method on nattokinase activity, biogenic amines, and sensory characteristics of natto
Abstract
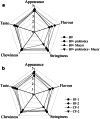
Nattokinase activity (NK), biogenic amine content and sensory properties of natto are of great significance to consumers, which are affected by strains and fermentation methods. In this study, changes in the pH, biogenic amine and free amino nitrogen (FAN) contents, NK and protease activities, and sensory characteristics of natto prepared using Bacillus subtilis GUTU09 combined with different strains (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and Mucor) and fermentation methods were investigated. The combination of two strains showed the best fermentation performance among all samples. The NK and protease activity and FAN content in double-strain fermentation increased by 10.33 FU/g, 88.78 U/g, and 2.34 g/kg, respectively, compared with those in single-strain fermentation. Sensory evaluation demonstrated that mixed fermentation primarily affected the sensory acceptance. This method also reduced the contents of various biogenic amines in natto compared with single-strain fermentation. Tyramine, cadaverine, spermine, and spermidine were significantly reduced, whereas histamine was slightly increased. The total biogenic amines decreased from 390.76 mg/kg to a minimum of 16.16 mg/kg. Some Mucor strains also reduced the contents of various biogenic amines. In the dual-bacteria fermentation of Mucor and GUTU09, co-fermentation has advantages over stage-fermentation, with higher NK and protease activity and higher sensory scores. Correlation analysis showed that the formation and accumulation of some biogenic amines in natto prepared using different microbial combinations were related to NK activity and pH. All these results showed that the quality of natto was improved by mixed fermentation and suitable fermentation methods, which laid a foundation for its potential industrial application.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis GUTU09; Biogenic amines; Combination fermentation; Nattokinase; Sensory evaluation.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adeyemo SM, Onilude AA. Enzymatic reduction of anti-nutritional factors in fermenting soybeans by Lactobacillus plantarum isolates from fermenting cereals. Niger Food J. 2013;31(2):84–90. doi: 10.1016/s0189-7241(15)30080-1. - DOI
-
- Ahmad A, Hayat I, Arif S, Masud T, Khalid N, Ahmed A. Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic effects of soybean (glycine max) Int J Food Prop. 2014;17(6):1332–1354. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2012.714828. - DOI
-
- Ali MW, Shahzad R, Bilal S, Adhikari B, Kim I-D, Lee J-D, Lee I-J, Kim BO, Shin D-H. Comparison of antioxidants potential, metabolites, and nutritional profiles of Korean fermented soybean (Cheonggukjang) with Bacillus subtilis KCTC 13241. J Food Sci Technol. 2018;55(8):2871–2880. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3202-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources