Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome: A rare diagnosis in children
- PMID: 33088541
- PMCID: PMC7563636
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.3165
Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome: A rare diagnosis in children
Abstract
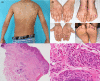
Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (IHES) is one of numerous hypereosinophilic syndromes. The incidence of IHES among children is unknown, but it is considered a rare disease. We report a pediatric case of IHES and the challenges to finding an effective treatment. The patient described here was responsive to prednisolone and thalidomide.
Keywords: hypereosinophilia; idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome; prednisolone; thalidomide.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Hardy WR, Anderson RE. The hypereosinophilic syndromes. Ann Intern Med. 1968;68(6):1220‐1229. - PubMed
-
- Kanthila J, Bhaskarand N. Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome in children: 3 cases with review of literature. Indian J Pediatr. 2013;80(2):124‐127. - PubMed
-
- Herández‐Benítez R, Vicencio‐Rivas J, Iglesias‐Leboreiro J, Martina‐Luna M, Madrazo‐Miranda MR, Lases‐Rufeil S. Hypereosinophilic syndrome in an infant. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2019;76:134‐137. - PubMed
-
- Podjasek JC, Butterfield JH. Mortality in hypereosinophilic syndrome: 19 years of experience of Mayo Clinic with a review of the literature. Leuk Res. 2013;37(4):392‐395. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

