Accuracy of the GENEActiv Device for Measuring Light Exposure in Sleep and Circadian Research
- PMID: 33089197
- PMCID: PMC7445795
- DOI: 10.3390/clockssleep2020012
Accuracy of the GENEActiv Device for Measuring Light Exposure in Sleep and Circadian Research
Abstract
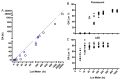
Light is a variable of key interest in circadian rhythms research, commonly measured using wrist-worn sensors. The GENEActiv Original is a cost-effective and practical option for assessing light in ambulatory settings. With increasing research on health and well-being incorporating sleep and circadian factors, the validity of wearable devices for assessing light environments needs to be evaluated. In this study, we tested the accuracy of the GENEActiv Original devices (n = 10) for recording light under a range of ecologically relevant lighting conditions, including LED, fluorescent, infrared, and outdoor lighting. The GENEActiv output had a strong linear relationship with photopic illuminance. However, the devices consistently under-reported photopic illuminance, especially below 100 lux. Accuracy below 100 lux depended on the light source, with lower accuracy and higher variability under fluorescent lighting. The device's accuracy was also tested using light sources of varying spectral composition, which indicated that the device tends to under-report photopic illuminance for green light sources and over-report for red light sources. Furthermore, measures of photopic illuminance were impacted by infrared light exposure. We conclude that the GENEActiv Original is suitable for mapping light patterns within an individual context, and can reasonably differentiate indoor vs. outdoor lighting, though the accuracy is variable at low light conditions. Given the human circadian system's high sensitivity to light levels below 100 lux, if using the GENEActiv Original, we recommend also collecting light source data to better understand the impact on the circadian system, especially where participants spend prolonged periods in dim lighting.
Keywords: actigraphy; ambulatory monitoring; chronobiology; dosimeter; light.
© 2020 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of InterestJES and EMM have no relevant financial conflicts of interest to report. ERFC is currently funded by an Innovation Connections Grant from the Australian Government, Department of Industry, Innovation and Science. SWC and AJKP are both investigators on projects funded by the Alertness Safety and Productivity CRC.
Figures


References
-
- Phillips A.J., Vidafar P., Burns A.C., McGlashan E.M., Anderson C., Rajaratnam S.M., Lockley S.W., Cain S.W. High sensitivity and interindividual variability in the response of the human circadian system to evening light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:12019–12024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901824116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

