Portosystemic shunts versus endoscopic intervention with or without medical treatment for prevention of rebleeding in people with cirrhosis
- PMID: 33089892
- PMCID: PMC8095029
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000553.pub3
Portosystemic shunts versus endoscopic intervention with or without medical treatment for prevention of rebleeding in people with cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: People with liver cirrhosis who have had one episode of variceal bleeding are at risk for repeated episodes of bleeding. Endoscopic intervention and portosystemic shunts are used to prevent further bleeding, but there is no consensus as to which approach is preferable.
Objectives: To compare the benefits and harms of shunts (surgical shunts (total shunt (TS), distal splenorenal shunt (DSRS), or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)) versus endoscopic intervention (endoscopic sclerotherapy or banding, or both) with or without medical treatment (non-selective beta blockers or nitrates, or both) for prevention of variceal rebleeding in people with liver cirrhosis.
Search methods: We searched the CHBG Controlled Trials Register; CENTRAL, in the Cochrane Library; MEDLINE Ovid; Embase Ovid; LILACS (Bireme); Science Citation Index - Expanded (Web of Science); and Conference Proceedings Citation Index - Science (Web of Science); as well as conference proceedings and the references of trials identified until 22 June 2020. We contacted study investigators and industry researchers.
Selection criteria: Randomised clinical trials comparing shunts versus endoscopic interventions with or without medical treatment in people with cirrhosis who had recovered from a variceal haemorrhage.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. When possible, we collected data to allow intention-to-treat analysis. For each outcome, we estimated a meta-analysed estimate of treatment effect across trials (risk ratio for binary outcomes). We used random-effects model meta-analysis as our main analysis and as a means of presenting results. We reported differences in means for continuous outcomes without a meta-analytic estimate due to high variability in their assessment among all trials. We assessed the certainty of evidence using GRADE.
Main results: We identified 27 randomised trials with 1828 participants. Three trials assessed TSs, five assessed DSRSs, and 19 trials assessed TIPSs. The endoscopic intervention was sclerotherapy in 16 trials, band ligation in eight trials, and a combination of band ligation and either sclerotherapy or glue injection in three trials. In eight trials, endoscopy was combined with beta blockers (in one trial plus isosorbide mononitrate). We judged all trials to be at high risk of bias. We assessed the certainty of evidence for all the outcome review results as very low (i.e. the true effects of the results are likely to be substantially different from the results of estimated effects). The very low evidence grading is due to the overall high risk of bias for all trials, and to imprecision and publication bias for some outcomes. Therefore, we are very uncertain whether portosystemic shunts versus endoscopy interventions with or without medical treatment have effects on all-cause mortality (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.13; 1828 participants; 27 trials), on rebleeding (RR 0.40, 95% CI 0.33 to 0.50; 1769 participants; 26 trials), on mortality due to rebleeding (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.76; 1779 participants; 26 trials), and on occurrence of hepatic encephalopathy, both acute (RR 1.60, 95% CI 1.33 to 1.92; 1649 participants; 24 trials) and chronic (RR 2.51, 95% CI 1.38 to 4.55; 956 participants; 13 trials). No data were available regarding health-related quality of life. Analysing each modality of portosystemic shunts individually (i.e. TS, DSRS, and TIPS) versus endoscopic interventions with or without medical treatment, we are very uncertain if each type of shunt has effect on all-cause mortality: TS, RR 0.46, 95% CI 0.19 to 1.13; 164 participants; 3 trials; DSRS, RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.33; 352 participants; 4 trials; and TIPS, RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.31; 1312 participants; 19 trial; on rebleeding: TS, RR 0.28, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.56; 127 participants; 2 trials; DSRS, RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.65; 330 participants; 5 trials; and TIPS, RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.55; 1312 participants; 19 trials; on mortality due to rebleeding: TS, RR 0.25, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.96; 164 participants; 3 trials; DSRS, RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.74; 352 participants; 5 trials; and TIPS, RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.04; 1263 participants; 18 trials; on acute hepatic encephalopathy: TS, RR 1.66, 95% CI 0.70 to 3.92; 115 participants; 2 trials; DSRS, RR 1.70, 95% CI 0.94 to 3.08; 287 participants; 4 trials, TIPS, RR 1.61, 95% CI 1.29 to 1.99; 1247 participants; 18 trials; and chronic hepatic encephalopathy: TS, Fisher's exact test P = 0.11; 69 participants; 1 trial; DSRS, RR 4.87, 95% CI 1.46 to 16.23; 170 participants; 2 trials; and TIPS, RR 1.88, 95% CI 0.93 to 3.80; 717 participants; 10 trials. The proportion of participants with shunt occlusion or dysfunction was overall 37% (95% CI 33% to 40%). It was 3% (95% CI 0.8% to 10%) following TS, 7% (95% CI 3% to 13%) following DSRS, and 47.1% (95% CI 43% to 51%) following TIPS. Shunt dysfunction in trials utilising polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents was 17% (95% CI 11% to 24%). Length of inpatient hospital stay and cost were not comparable across trials. Funding was unclear in 16 trials; 11 trials were funded by government, local hospitals, or universities.
Authors' conclusions: Evidence on whether portosystemic shunts versus endoscopy interventions with or without medical treatment in people with cirrhosis and previous hypertensive portal bleeding have little or no effect on all-cause mortality is very uncertain. Evidence on whether portosystemic shunts may reduce bleeding and mortality due to bleeding while increasing hepatic encephalopathy is also very uncertain. We need properly conducted trials to assess effects of these interventions not only on assessed outcomes, but also on quality of life, costs, and length of hospital stay.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00570973 NCT01326949 NCT00690027 NCT02477384 NCT03094234.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
RGS: nothing to declare. GP: nothing to declare. HLR: nothing to declare. NRB: nothing to declare. MOW: nothing to declare. RS: nothing to declare. SK: nothing to declare.
Figures
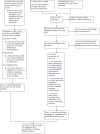
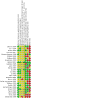
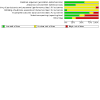
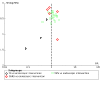
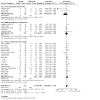
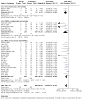
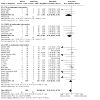

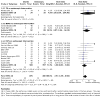
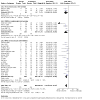
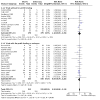
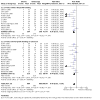
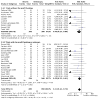

Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000553.pub2
References
References to studies included in this review
Cabrera 1996 {published data only}
Cello 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cello JP, Ring EJ, Olcott EW, Koch J, Gordon R, Sandhu J, et al. Endoscopic sclerotherapy compared with percutaneous transjugular Intrahepatic portosystemic shunt after initial sclerotherapy in patients with acute variceal haemorrhage. A randomised controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997;126(11):858-65. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-11-199706010-00002] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Dunne 2020 {published data only}
-
- Dunne PDJ, Sinha R, Stanley AJ, Lachlan N, Ireland H, Shams A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: standard of care versus early-transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt (TIPSS) in patients with cirrhosis and oesophageal variceal bleeding. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2020;52(1):98-106. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ferlitsch 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ferlitsch A, Ulbrich G, Maieron A, Salzl P, Reiberger T, Payer BA, et al. A randomized, controlled, multicentre trial comparing endoscopic band ligation versus tips in cirrhotic patients with recurrent variceal bleeding non-responding to pharmacological therapy. Journal of Hepatology 2012;56(Suppl 2):S555.
García‐Villarreal 1999 {published data only}
-
- García-Villarreal L, Martinez-Lagares F, Sierra A, Guevara C, Marrero JM, Jiménez E, et al. Transjugular Intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus prevention of rebleeding after recent variceal hemorrhage. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1999;29(1):27-32. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.510290125] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
GDEAIH 1995 {published data only}
-
- Groupe d'Etude de Anastomoses Intra-Hepatiques. TIPS versus sclerotherapy + propranolol in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: preliminary results of a multicenter randomised trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1995;22(S4):297A.
Gülberg 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gülberg N, Schepke G, Geigenberger G, Holl J, Brensing KA, Waggershauser T, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting is not superior to endoscopic variceal band ligation for prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2002;37(3):338-43. [DOI: 10.1080/003655202317284255] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Henderson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Henderson JM, Kutner MH, Millikan WJ, Galambos JT, Riepe SP, Brooks S, et al. Endoscopic variceal sclerosis compared with distal splenorenal shunt to prevent recurrent variceal bleeding in cirrhosis, a prospective randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1990;112(4):262-9. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-262] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Warren WD, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ, Galambos JT, Brooks WS, Riepe SP, et al. Distal splenorenal shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy for long-term management of variceal bleeding: preliminary report of a prospective, randomised trial. Annals of Surgery 1986;203(5):454-62. [DOI: 10.1097/00000658-198605000-00002] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Holster 2016 {published data only}
-
- Harki J, Holster IL, Polinder S, Moelker A, Van Buuren HR, Kuipers EJ, et al. Cost effectiveness of covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) versus endoscopic treatment for secondary prevention of gastro-oesophageal variceal rebleeding. Gastroenterology 2016;150(4 Suppl 1):S1160.
-
- Harki J, Holster LI, Polinder S, Moelker A, Van Buuren HR, Kuipers EJ, et al. Cost effectiveness of covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic treatment for secondary prevention of gastro-oesophageal variceal bleeding. Journal of Hepatology 2016;64(2 Suppl):S265-6. [DOI: ]
-
- Holster IL, Moelker A, Tjwa ET, Wils A, Kupers EJ, Pattynama P, et al. Early transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) as compared to endoscopic treatment reduces rebleeding but not mortality in cirrhotic patients with a 1st or 2nd episode of variceal bleeding: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. United European Gastroenterology Journal 2013;1(S1):A84.
-
- Holster IL, Tjwa ETTL, Moelker A, Wils A, Hansen BE, Vermeijden JR, et al. Covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy + ß-blocker for prevention of variceal rebleeding. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2016;63(2):581-9. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.28318] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Isaksson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Isaksson B, Jeppsson B, Bengtsson F, Hannesson P, Herlin P, Bengmark S. Mesocaval shunt or repeated sclerotherapy: effects on rebleeding and encephalopathy - a randomized trial. Surgery 1995;117(5):498-504. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jalan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jalan R, Forrest EH, Redhead DN, Dillon JF, Bzeizi KI, Finlayson NDC, et al. TIPSS vs variceal band ligation in the secondary prevention of variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis: preliminary results of a randomised, controlled study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1995;22(4):251A.
-
- Jalan R, Forrest EH, Stanley AJ, Redhead DN, Forbes J, Dillon JF, et al. A randomized trial comparing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt with variceal band ligation in the prevention of rebleeding from esophageal varices. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1997;26(5):1115-22. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.510260505] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Korula 1987 {published data only}
-
- Korula J, Yelin A, Yamada S, Weiner J, Cohen H, Reynolds TB. A prospective randomised controlled comparison of chronic endoscopic variceal sclerotherapy and portalsystemic shunt for variceal hemorrhage in Child's Class A cirrhotics: a preliminary report. Gastroenterology 1987;92:1745.
Lo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lo GH, Liang HL, Chen WC, Chen MH, Lai KH, Hsu PI, et al. A prospective, randomized controlled trial of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus cyanoacrylate injection in the prevention of gastric variceal rebleeding. Endoscopy 2007;39(8):679-85. [DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-966591] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Luo 2015 {published data only}
-
- Luo X, Wang Z, Tsauo J, Zhou B, Zhang H, Li Z. Advanced cirrhosis combined with portal vein thrombosis: a randomized trial of TIPS versus endoscopic band ligation plus propranolol for the prevention of recurrent esophageal variceal bleeding. Radiology 2015;276(1):286-93. [DOI: 10.1148/radiol.15141252] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Lv 2018 {published data only}
-
- Lv Y, Qi X, He C, Wang Z, Yin Z, Niu J, et al. Covered TIPS versus endoscopic band ligation plus propranolol for the prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients with portal vein thrombosis: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2018;67(12):2156-68. [DOI: 10.1136/ gutjnl-2017-314634] [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Merli 1998 {published data only}
-
- Merli M, Riggio O, Capoccaccia L, Ziparo V, Bolognese A, Rossi P, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) vs endoscopic sclerotherapy (ES) in preventing variceal rebleeding preliminary results of a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1994;20(4):A107.
-
- Merli M, Salerno F, Riggio O, Franchis R, Fiaccadori F, Meddi P, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a randomized multicenter trial. Gruppo Italiano Studio TIPS (G.I.S.T.). Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1998;27(1):48-53. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.510270109] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rossi P, Maccioni F, Salvatori FM, Bezzi M, Gandini R, Broglia L, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): indications and results after 22 months of experience [Derivazione porto-sistemica intraepatica transgiugulare (TIPS): indicazioni e risultati dopo 22 anni di esperienza]. Radiologica Medica 1994;87(5):585-96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Narahara 2001 {published data only}
-
- Narahara Y, Kanazawa H, Kawamata H, Tada N, Saitoh H, Matsuzaka S, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with endoscopic sclerotherapy in the long-term management of patients with cirrhosis after recent variceal hemorrhage. Hepatology Research 2001;21(3):189-98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Planas 1991 {published data only}
Pomier‐Layrargues 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pomier-Layrargues G, Dufresne MP, Buli B, Lambert J, Fenyves D, Willems B, et al. TIPS versus endoscopic variceal ligation in the prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients: a comparative randomized clinical trial (interm analysis). Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1997;26(4):137A.
-
- Pomier-Layrargues G, Villeneuve JP, Deschenes M, Bui B, Perreault P, Fenyves D, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) versus endoscopic variceal ligation in the prevention of variceal rebleeding in patients with cirrhosis: a randomised trial. Gut 2001;48(3):390-6. [DOI: 10.1136/gut.48.3.390] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Rikkers 1993 {published data only}
Rossle 1997 {published data only}
-
- Rossle M, Deibert P, Haag K, Ochs A, Olschewski M, Siegerstetter V, et al. Randomised trial of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopy plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding. Lancet 1997;349(9058):1043-9. [DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)08189-5] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Santambrogio 2006 {published data only}
-
- Santambrogio R, Opocher E, Costa M, Bruno S, Caretti AP, Spina GP. Natural history of a randomized trial comparing distal spleno-renal shunt with endoscopic sclerotherapy in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: a lesson from the past. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2006;12(39):6331-8. [DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6331] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sanyal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sanyal AJ, Freedman AM, Luketic VA, Purdum PP 3rd, Shiffman ML, Cole PE, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts compared with endoscopic sclerotherapy for the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage. A randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997;126(11):849-57. [DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-11-199706010-00001] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Sauer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Krieger S, Jauss M, Jansen O, Stiehl A, Sauer P, Geissler M, et al. MRI findings in chronic hepatic encephalopathy depend on portosystemic shunt: results of a controlled prospective clinical investigation. Journal of Hepatology 1997;27(1):121-6. [DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80290-5] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Sauer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sauer P, Benz C, Theilmann G, Richter W, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPS) vs. endoscopic banding in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: final results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology 1998;114(4):A1334.
-
- Sauer P, Hansmann J, Richter G, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPS) vs. endoscopic banding in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: a long-term randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2000;118(4 Pt 2):A1485.
-
- Sauer P, Theilmann L, Benz C, Richter G, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPS) vs. endoscopic banding in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: interim analysis of a randomized study. Gastroenterology 1997;112(4):A1374. - PubMed
Terés 1987 {published data only}
-
- Terés J, Bordas JM, Bravo D, Visa J, Grande L, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, et al. Sclerotherapy vs. distal splenorenal shunt in the elective treatment of variceal hemorrhage: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1987;7(3):430-6. [DOI: DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840070303] [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Urbistondo 1996 {published data only}
-
- Urbistondo M, Torres EA, Castro F, Oharriz J, Medina R, Molina A, et al. Prevention of recurrent esophageal bleeding and survival in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: a randomized study. Puerto Rico Health Sciences Journal 1996;15(3):195-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cello 1982 {published data only}
-
- Cello JP, Crass RC, Trunkey DD. Endoscopic sclerotherapy versus esophageal transection of Child's class C patients with variceal hemorrhage. Comparison with results of portacaval shunt: preliminary report. Surgery 1982;91(3):333-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cello 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cello J P, Grendell JH, Crass RA, Weber TE, Trunkey DD. Endoscopic sclerotherapy versus portacaval shunt in patients with severe cirrhosis and acute variceal hemorrhage. Long-term follow-up. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;316(1):11-5. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198701013160103] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Escorsell 2002 {published data only}
-
- Escorsell A, Bañares R, García-Pagán JC, Gilabert R, Moitinho E, Piqueras B, et al. TIPS versus drug therapy in preventing variceal rebleeding in advanced cirrhosis: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002;35(2):385-92. [DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2002.30418] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Garcia‐Pagan 2010 {published data only}
Kitano 1992 {published data only}
-
- Kitano S, Iso Y, Hashizume M, Yamaga H, Koyanagi N, Wada H, et al. Sclerotherapy vs. esophageal transection vs. distal splenorenal shunt for the clinical management of esophageal varices in patients with child class A and B liver function: a prospective randomized trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1992;15(1):63-8. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840150113] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Li 2015 {published data only}
Meddi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Meddi P, Merli M, Lionetti R, De Santis A, Valeriano V, Masini A, et al. Cost analysis for the prevention of variceal rebleeding: a comparison between transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and endoscopic sclerotherapy in a selected group of Italian cirrhotic patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1999;29(4):1074-7. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.510290411] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Orloff 1994 {published data only}
-
- Orloff MJ, Bell RH, Orloff MS, Hardison WGM, Greenburg AG. Prospective randomized trial of emergency portacaval shunt and emergency medical therapy in unselected cirrhotic patients with bleeding varices. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1994;20(4 Pt 1):863-72. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840200414] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Orloff 2009 {published data only}
-
- Orloff M, Isenberg J, Wheeler H, Haynes K, Jinich-Brook H, Rapier R, et al. Portal-systemic encephalopathy in a randomized controlled trial of endoscopic sclerotherapy versus emergency portacaval shunt treatment of acutely bleeding esophageal varices in cirrhosis. Annals of Surgery 2009;250(4):598-610. [DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b73126] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Orloff MJ, Isenberg JI, Wheeler HO, Haynes KS, Jinich-Brook H, Rapier R, et al. Direct costs of care in a randomized controlled trial of endoscopic sclerotherapy versus emergency portacaval shunt for bleeding esophageal varices in cirrhosis - Part 4. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2011;15(1):38-47. [DOI: 10.1007/s11605-010-1332-6] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orloff MJ, Isenberg JI, Wheeler HO, Haynes KS, Jinich-Brook H, Rapier R, et al. Emergency portacaval shunt versus rescue portacaval shunt in a randomized controlled trial of emergency treatment of acutely bleeding esophageal varices in cirrhosis - Part 3. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2010;14(11):1782-95. [DOI: 10.1007/s11605-010-1279-7] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Orloff 2015 {published data only}
-
- Orloff MJ, Hye RJ, Wheeler HO, Isenberg JI, Haynes KS, Vaida F, et al. Randomized trials of endoscopic therapy and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus portacaval shunt for emergency and elective treatment of bleeding gastric varices in cirrhosis. Surgery 2015;157(6):1028-45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orloff MJ, Isenberg JI, Wheeler HO, Haynes KS, Jinich-Brook H, Rapier R, et al. Randomized trial of emergency endoscopic sclerotherapy versus emergency portacaval shunt for acutely bleeding esophageal varices in cirrhosis. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2009;209(1):25-40. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.02.059] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Paquet 1990 {published data only}
-
- Paquet KJ, Lazar A, Gad HA. Surgical measures in recurrent hemorrhage from esophageal and gastric varices after sclerotherapy - a prospective study [Chirurgische Massnahmen bei Rezidivblutungen aus Osophagus- und Magenvarizen nach Sklerosierungstherapie - eine prospektive Studie]. Langenbecks Archiv für Chirurgie. Supplement II, Verhandlungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Chirurgie 1990;Suppl II:397-402. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Resnick 1974 {published data only}
-
- Resnick RH, Iber FL, Ishihara AM, Chalmers TC, Zimmerman H. A controlled study of the therapeutic portacaval shunt. Gastroenterology 1974;6(5):843-57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reynolds 1981 {published data only}
-
- Reynolds TB, Donovan AJ, Mikkelsen WP, Redeker AG, Turrill FL, Weiner JM. Results of a 12-year randomized trial of portacaval shunt in patients with alcoholic liver disease and bleeding varices. Gastroenterology 1981;80(5 Pt 1):1005-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sanyal 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sanyal AJ, Freedman AM, Shiffman ML, Purdum PP 3rd, Luketic VA, Cheatham AK. Portosystemic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: results of a prospective controlled study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1994;20(1 Pt 1):46-55. [DOI: 10.1016/0270-9139(94)90133-3] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sauer P, Theilmann L, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPS) [Hepatische Enzephalopathie nach transjugularem intrahepatischem porto-systemischem Stent-Shunt (TIPS)]. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 1995;33(5):277-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sauerbruch 2015 {published data only}16334693
-
- Sauerbruch T, Mengel M, Dollinger M, Zipprich A, Rossle M, Panther E, et al, German Study Group for Prophaxis of Variceal Rebleeding. Prevention of rebleeding from esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis receiving small-diameter stents versus hemodynamically controlled medical therapy. Gastroenterology 2015;149(3):660-8. [MEDLINE: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.05.011] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Terés 1987a {published data only}
-
- Terés J, Baroni R, Bordas JM, Visa J, Pera C, Rodes J. Randomized trial of portacaval shunt, stapling transection and endoscopic sclerotherapy in uncontrolled variceal bleeding. Journal of Hepatology 1987;4(2):159-67. [DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80075-2] [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tripathi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tripathi D, Helmy A, Lui HF, Stanley AJ, Forrest E, Redhead DN, et al. Randomized controlled trial of transjugular intra-hepatic portosystemic stent-shunt (TIPSS) versus TIPSS and variceal band ligation (VBL) in the prevention of variceal re-bleeding. Journal of Hepatology 2001;34(Suppl 1):69-70. [DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(01)81114-4] - DOI
References to studies awaiting assessment
Lv 2019 {published data only}
-
- Lv Y, Yang Z, Liu L, Li K, He C, Wang Z, et al. Early TIPS with covered stents versus standard treatment for acute variceal bleeding in patients with advanced cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2019;4(8):587-98. [DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30090-1] [MEDLINE: ] [NCT01370161] - DOI - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT02477384 {published data only}
-
- NCT02477384. 8mm-TIPS versus endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding [Randomised trial of 8mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic variceal ligation plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02477384 (first received 15 June 2015).
NCT03094234 {published data only}
-
- NCT03094234. 8mm-TIPS versus endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding in patients with child A cirrhosis. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03094234 (first received 23 March 2017).
Additional references
Bari 2012
Bernard 1997
Brok 2008
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta-analyses may be inconclusive - trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287-98. [DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn188] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Brown 1997
-
- Brown RS Jr, Lake JR. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt as a form of treatment for portal hypertension: indications and contraindications. Advances in Internal Medicine 1997;42:485-504. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bureau 2007
-
- Bureau C , Pagan JC, Layrargues GP, Metivier S, Bellot P, Perreault P, et al. Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluoroethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomized multicentre study. Liver International 2007;27(6):742-7. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01522.x] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Burroughs 2002
-
- Burroughs AK, Vangeli M. Transjugular Intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy: randomized trials for secondary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding: an updated meta-analysis. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2002;37(3):249-52. [DOI: 10.1080/003655202317284138] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Cabonell 2004
Casado 1998
-
- Casado M, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bru C, Banares R, Bandi JC, et al. Clinical events after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: correlation with hemodynamic findings. Gastroenterology 1998;114(6):1296-303. [MEDLINE: ] [10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70436-6] - PubMed
Castellini 2018
Collins 1995
Cordon 2012
D'Amico 1995
D'Amico 2004
-
- D'Amico G. Esophageal varices: from appearance to rupture; natural history and prognostic indicators. In: Groszmann RJ, Bosch J (Editors). Portal Hypertension in the 21st Century. King's College London, UK: Springer, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004.
Dai 2015
de Franchis 2010
de Franchis 2015
EASL 2018
Egger 1997
Garcia‐Tsao 2007
-
- Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey WD, The Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Association of the Study of Liver Diseases, The Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2007;46(3):922-38. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.21907] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Garcia‐Tsao 2017
-
- Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2017;65(1):310-35. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Gartlehner 2019
Grace 1997
-
- Grace ND. Diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to portal hypertension. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1997;92(7):1081-91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 4 April 2020. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015. Available at gradepro.org.
Graham 1981
-
- Graham DY, Smith JL. The course of patients after variceal haemorrhage. Gastroenterology 1981;80(4):800-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Herrera 2014
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2019
-
- Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated August 2019). Cochrane, 2019. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Jakobsen 2014
LaBerge 1993
Laine 1995
Luca 1999
McIntyre 1996
-
- McIntyre N, Burroughs AK. Cirrhosis and portal hypertension. In: Weatherall DJ, Ledingham JGG, Warrell DA, editors(s). Oxford Textbook of Medicine. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone, 1996:2085-100.
Papatheodoridis 1999
-
- Papatheodoridis GV, Goulis J, Leandro G, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt compared with endoscopic treatment for prevention of variceal rebleeding: a meta-analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1999;30(3):612-22. [DOI: 10.1002/hep.510300316] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Parmar 1998
Puente 2014
Pugh 1973
-
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. British Journal of Surgery 1973;60(8):646-9. [MEDLINE: ] [10.1002/bjs.1800600817] - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014. https://community.cochrane.org/help/tools-and-software/revman-5.
Rosemurgy 2012
-
- Rosemurgy AS, Frohman HA, Teta AF, Luberice K, Ross SB. Prosthetic H-graft portacaval shunts vs transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts: 18-year follow-up of a randomized trial. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2012;214(4):445-53. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.12.042] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Royle 2003
Sauer 1998
-
- Sauer P, Benz C, Theilmann G, Richter W, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Tranjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPS) vs. endoscopic banding in the prevention of variceal rebleeding: final results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology 1998;114(1):A1334.
Savović 2018
Shi 2013
Simmonds 2015
Spina 1992a
-
- Spina GP, Henderson JM, Rikkers LF, Teres J, Burroughs AK, Conn HO, et al. Distal spleno-renal shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy in the prevention of variceal rebleeding. A meta-analysis of 4 randomized clinical trials. Journal of Hepatology 1992;16(3):338-45. [DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80666-x] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Terblanche 1983
-
- Terblanche J, Bornman PC, Kahn D, Jonker MA, Campbell JA, Wright J, et al. Failure of repeated injection sclerotherapy to improve long-term survival after oesophageal variceal bleeding. A five-year prospective controlled clinical trial. Lancet 1983;2(8363):1328-32. [DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91090-5] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Thiele 2012
Thorlund 2010
-
- Thorlund K, Anema A, Mills E. Interpreting meta-analysis according to the adequacy of sample size. An example using isoniazid chemoprophylaxis for tuberculosis in purified protein derivative negative HIV-infected individuals. Clinical Epidemiology 2010;2:57-66. [MEDLINE: ] [10.2147/clep.s9242] - PMC - PubMed
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/tsa/files/tsa_manual.pdf 2011 (accessed June 2019).
Tierney 2007
Tripathi 2015
TSA 2011 [Computer program]
-
- TSA - Trial Sequential Analysis. Version 0.9.5.10 Beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2011. www.ctu.dk/tsa/downloads.aspx.
Tudur 2001
-
- Tudur C, Williamson PR, Khan S, Best LY. The value of the aggregate data approach in meta-analysis with time-to-event outcomes. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) 2001;2(164):357-70. [DOI: 10.1111/1467-985X.00207] - DOI
Villanueva 2008
-
- Villanueva C, Balanzo J. Variceal bleeding: pharmacological treatment and prophylactic strategies. Drugs 2008;68(16):2303-24. [DOI: 10.2165/0003495-200868160-00004] [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Warren 1986
Wetterslev 2008
Wetterslev 2009
Wetterslev 2017
Williamson 2002
Zhao 2014
Zheng 2008
-
- Zheng M, Chen Y, Bai J, Zeng Q, You J, Jin R, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy in the secondary prophylaxis of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients: meta-analysis update. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2008;42(5):507-15. [DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31815576e6] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PubMed
Zhou 2019
-
- Zhou GP, Sun LY, Wei L, Qu W, Zeng ZG, Liu Y, et al. Comparision between portosystemic shunts and endoscopic therapy for prevention of variceal re-bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chinese Medical Journal 2019;132(9):1087-99. [DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000212] [MEDLINE: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Khan 1997
Khan 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

