The SIRT6 activator MDL-800 improves genomic stability and pluripotency of old murine-derived iPS cells
- PMID: 33089974
- PMCID: PMC7431819
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13185
The SIRT6 activator MDL-800 improves genomic stability and pluripotency of old murine-derived iPS cells
Abstract
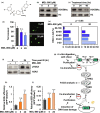
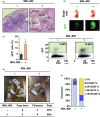
Cellular reprogramming is an emerging strategy for delaying the aging processes. However, a number of challenges, including the impaired genome integrity and decreased pluripotency of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from old donors, may hinder their potential clinical applications. The longevity gene, Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6), functions in multiple biological processes such as the maintenance of genome integrity and the regulation of somatic cell reprogramming. Here, for the first time, we demonstrate that MDL-800, a recently developed selective SIRT6 activator, improved genomic stability by activating two DNA repair pathways-nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and base excision repair (BER) in old murine-derived iPSCs. More interestingly, we found that pretreating old murine iPSCs, which normally exhibit a restricted differentiation potential, with MDL-800 promoted the formation of teratomas comprised of all three germ layers and robustly stimulated chimera generation. Our findings suggest that pharmacological activation of SIRT6 holds great promise in treating aging-associated diseases with iPSC-based cell therapy.
Keywords: DNA repair; MDL-800; SIRT6; aging; genome integrity; pluripotency.
© 2020 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Etchegaray, J. P. , Chavez, L. , Huang, Y. , Ross, K. N. , Choi, J. , Martinez‐Pastor, B. , … Mostoslavsky, R. (2015). The histone deacetylase SIRT6 controls embryonic stem cell fate via TET‐mediated production of 5‐hydroxymethylcytosine. Nature Cell Biology, 17(5), 545–557. 10.1038/ncb3147 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

