Ovarian Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Differential Expression Genes Associated with Cell Death Process after Selection for Ovulation Rate in Rabbits
- PMID: 33092110
- PMCID: PMC7593938
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10101924
Ovarian Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Differential Expression Genes Associated with Cell Death Process after Selection for Ovulation Rate in Rabbits
Abstract
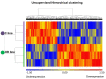
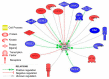
Litter size is an essential trait in rabbit meat production but with low heritability. A selection experiment for ovulation rate has been performed for 10 generations to improve litter size in rabbits. The selected line increased two ova more than the control line but nevertheless a negative correlation was observed with prenatal survival. A transcriptomic study was performed, using microarrays, in ovarian tissue from females belonging to the selected line and the control line. Our results showed 1357 differential expressed genes and nineteen potential biomarkers associated with prenatal mortality, which could explain differences between litter size in rabbits. Cell death was the most relevant process.
Keywords: litter size; ovarian tissue; ovulation rate; rabbit; transcriptomic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Direct and correlated responses to two-stage selection for ovulation rate and number of fully formed pigs at birth in swine.J Anim Sci. 2001 Sep;79(9):2286-97. doi: 10.2527/2001.7992286x. J Anim Sci. 2001. PMID: 11583415
-
Selection for ovulation rate in rabbits: direct and correlated responses estimated with a cryopreserved control population.J Anim Sci. 2012 Oct;90(10):3392-7. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-4837. Epub 2012 May 14. J Anim Sci. 2012. PMID: 22585826
-
Selection for ovulation rate in rabbits: genetic parameters, direct response, and correlated response on litter size.J Anim Sci. 2011 Oct;89(10):2981-7. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-3906. Epub 2011 May 27. J Anim Sci. 2011. PMID: 21622874
-
Influencing prolificacy of sows by selection for physiological factors.J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1985;33:139-49. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1985. PMID: 3910821 Review.
-
Genetic variation in prenatal survival and litter size.J Anim Sci. 1979;49 Suppl 2:66-74. doi: 10.1093/ansci/49.supplement_ii.66. J Anim Sci. 1979. PMID: 400778 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

