Contribution of miRNAs, tRNAs and tRFs to Aberrant Signaling and Translation Deregulation in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33092114
- PMCID: PMC7593945
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12103056
Contribution of miRNAs, tRNAs and tRFs to Aberrant Signaling and Translation Deregulation in Lung Cancer
Abstract
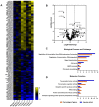
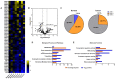
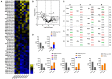
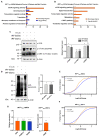
Transcriptomics profiles of miRNAs, tRNAs or tRFs are used as biomarkers, after separate examination of several cancer cell lines, blood samples or biopsies. However, the possible contribution of all three profiles on oncogenic signaling and translation as a net regulatory effect, is under investigation. The present analysis of miRNAs and tRFs from lung cancer biopsies indicated putative targets, which belong to gene networks involved in cell proliferation, transcription and translation regulation. In addition, we observed differential expression of specific tRNAs along with several tRNA-related genes with possible involvement in carcinogenesis. Transfection of lung adenocarcinoma cells with two identified tRFs and subsequent NGS analysis indicated gene targets that mediate signaling and translation regulation. Broader analysis of all major signaling and translation factors in several biopsy specimens revealed a crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways and downstream activation of eIF4E and eEF2. Subsequent polysome profile analysis and 48S pre-initiation reconstitution experiments showed increased global translation rates and indicated that aberrant expression patterns of translation initiation factors could contribute to elevated protein synthesis. Overall, our results outline the modulatory effects that possibly correlate the expression of important regulatory non-coding RNAs with aberrant signaling and translation deregulation in lung cancer.
Keywords: lung cancer; miRNAs; signaling; tRFs; tRNAs; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
tRFs: miRNAs in disguise.Gene. 2016 Apr 1;579(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.12.058. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26743126 Review.
-
tRNA Fragments Show Intertwining with mRNAs of Specific Repeat Content and Have Links to Disparities.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 15;79(12):3034-3049. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0789. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30996049 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tRNA‑derived fragments in colon cancer by comprehensive small RNA sequencing.Oncol Rep. 2019 Aug;42(2):735-744. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7178. Epub 2019 May 31. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173257
-
tRNA-derived fragments and tRNA halves: The new players in cancers.Cancer Lett. 2019 Jun 28;452:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30905816
-
Translation regulation in skin cancer from a tRNA point of view.Epigenomics. 2019 Feb;11(2):215-245. doi: 10.2217/epi-2018-0176. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Epigenomics. 2019. PMID: 30565492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial tRNA-Derived Fragments and Their Contribution to Gene Expression Regulation.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 3;12:729452. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.729452. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34539450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Noncoding RNAs in Regulation of Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 28;24(11):9414. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119414. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Prognostic Model Based on Seven Necroptosis-Related miRNAs for Predicting the Overall Survival of Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 24;2022:3198590. doi: 10.1155/2022/3198590. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35372581 Free PMC article.
-
High Intratumoral i-tRF-GlyGCC Expression Predicts Short-Term Relapse and Poor Overall Survival of Colorectal Cancer Patients, Independent of the TNM Stage.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 8;11(7):1945. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071945. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509584 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of tRNA-Derived Fragments in Cancer: Updates and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 17;26(12):5822. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125822. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

