Poxviral Targeting of Interferon Regulatory Factor Activation
- PMID: 33092186
- PMCID: PMC7590177
- DOI: 10.3390/v12101191
Poxviral Targeting of Interferon Regulatory Factor Activation
Abstract
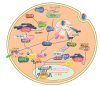
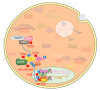
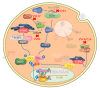
As viruses have a capacity to rapidly evolve and continually alter the coding of their protein repertoires, host cells have evolved pathways to sense viruses through the one invariable feature common to all these pathogens-their nucleic acids. These genomic and transcriptional pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) trigger the activation of germline-encoded anti-viral pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that can distinguish viral nucleic acids from host forms by their localization and subtle differences in their chemistry. A wide range of transmembrane and cytosolic PRRs continually probe the intracellular environment for these viral PAMPs, activating pathways leading to the activation of anti-viral gene expression. The activation of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NFκB) and Interferon (IFN) Regulatory Factor (IRF) family transcription factors are of central importance in driving pro-inflammatory and type-I interferon (TI-IFN) gene expression required to effectively restrict spread and trigger adaptive responses leading to clearance. Poxviruses evolve complex arrays of inhibitors which target these pathways at a variety of levels. This review will focus on how poxviruses target and inhibit PRR pathways leading to the activation of IRF family transcription factors.
Keywords: immune evasion; innate immune response; interferon regulatory factor; poxvirus; virus-host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate immune activation of NFκB and its antagonism by poxviruses.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):611-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25081317 Review.
-
Advances on Innate Immune Evasion by Avian Immunosuppressive Viruses.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:901913. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901913. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumour viruses and innate immunity.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Oct 19;372(1732):20160267. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0267. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28893934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Sensing of Parapoxvirus Orf Virus and Viral Immune Evasion.Viruses. 2025 Apr 19;17(4):587. doi: 10.3390/v17040587. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40285029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of cellular innate antiviral signaling by ubiquitin modification.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Mar;47(3):149-55. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmu133. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015. PMID: 25651846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of cytokines in poxvirus host tropism and adaptation.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Dec;57:101286. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2022.101286. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 36427482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinia Virus: Mechanisms Supporting Immune Evasion and Successful Long-Term Protective Immunity.Viruses. 2024 May 29;16(6):870. doi: 10.3390/v16060870. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molluscum contagiosum virus protein MC089 inhibits interferon regulatory factor 3 activation.J Gen Virol. 2024 Aug;105(8):002015. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.002015. J Gen Virol. 2024. PMID: 39167082
-
Special Issue: "Innate Immune Sensing of Viruses and Viral Evasion".Viruses. 2021 Mar 26;13(4):567. doi: 10.3390/v13040567. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33810623 Free PMC article.
-
Innate and adaptive immune responses that control lymph-borne viruses in the draining lymph node.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Sep;21(9):999-1007. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01188-0. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38918577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

