Myofunctional Therapy App for Severe Apnea-Hypopnea Sleep Obstructive Syndrome: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33093013
- PMCID: PMC7683258
- DOI: 10.2196/23123
Myofunctional Therapy App for Severe Apnea-Hypopnea Sleep Obstructive Syndrome: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Myofunctional therapy has demonstrated efficacy in treating sleep-disordered breathing. We assessed the clinical use of a new mobile health (mHealth) app that uses a smartphone to teach patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) to perform oropharyngeal exercises.
Objective: We conducted a pilot randomized trial to evaluate the effects of the app in patients with severe OSAHS.
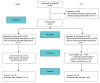
Methods: Forty patients with severe OSAHS (apnea-hypoxia index [AHI]>30) were enrolled prospectively and randomized into an intervention group that used the app for 90 sessions or a control group. Anthropometric measures, Epworth Sleepiness Scale (0-24), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (0-21), Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI) scores, and oxygen desaturation index were measured before and after the intervention.
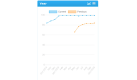
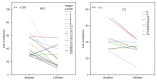
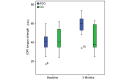
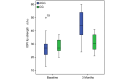
Results: After the intervention, 28 patients remained. No significant changes were observed in the control group; however, the intervention group showed significant improvements in most metrics. AHI decreased by 53.4% from 44.7 (range 33.8-55.6) to 20.88 (14.02-27.7) events/hour (P<.001). The oxygen desaturation index decreased by 46.5% from 36.31 (27.19-43.43) to 19.4 (12.9-25.98) events/hour (P=.003). The IOPI maximum tongue score increased from 39.83 (35.32-45.2) to 59.06 (54.74-64.00) kPa (P<.001), and the IOPI maximum lip score increased from 27.89 (24.16-32.47) to 44.11 (39.5-48.8) kPa (P<.001). The AHI correlated significantly with IOPI tongue and lip improvements (Pearson correlation coefficient -0.56 and -0.46, respectively; both P<.001). The Epworth Sleepiness Scale score decreased from 10.33 (8.71-12.24) to 5.37 (3.45-7.28) in the app group (P<.001), but the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index did not change significantly.
Conclusions: Orofacial exercises performed using an mHealth app reduced OSAHS severity and symptoms, and represent a promising treatment for OSAHS.
Trial registration: Spanish Registry of Clinical Studies AWGAPN-2019-01, ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04438785; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04438785.
Keywords: apnea; app; efficacy; mHealth; myofunctional therapy; oropharyngeal exercises; randomized trial; sleep; sleep apnea; smartphone app; therapy.
©Carlos O'Connor-Reina, Jose Maria Ignacio Garcia, Elisa Rodriguez Ruiz, Maria Del Carmen Morillo Dominguez, Victoria Ignacio Barrios, Peter Baptista Jardin, Juan Carlos Casado Morente, Maria Teresa Garcia Iriarte, Guillermo Plaza. Originally published in JMIR mHealth and uHealth (http://mhealth.jmir.org), 09.11.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: CR is the creator of, and has financial interest in, the AirwayGym app. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preliminary Assessment of an Ambulatory Device Dedicated to Upper Airway Muscle Training in Patients With Sleep Apnea: Proof-of-Concept Study.JMIR Biomed Eng. 2024 Apr 15;9:e51901. doi: 10.2196/51901. JMIR Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38875673 Free PMC article.
-
Sensorimotor tongue evaluation and rehabilitation in patients with sleep-disordered breathing: a novel approach.J Oral Rehabil. 2021 Dec;48(12):1363-1372. doi: 10.1111/joor.13247. Epub 2021 Oct 18. J Oral Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 34409644
-
Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 May 15;179(10):962-6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200806-981OC. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19234106 Clinical Trial.
-
Orofacial Myofunctional Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Laryngoscope. 2024 Jan;134(1):480-495. doi: 10.1002/lary.30974. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Laryngoscope. 2024. PMID: 37606313
-
[The treatment progress of myofunctional therapy for obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Apr;32(8):629-633. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.08.019. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29798153 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The effect of tongue elevation muscle training in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomised controlled trial.J Oral Rehabil. 2022 Nov;49(11):1049-1059. doi: 10.1111/joor.13369. Epub 2022 Sep 21. J Oral Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 36081312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Breathing Re-Education and Phenotypes of Sleep Apnea: A Review.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 26;10(3):471. doi: 10.3390/jcm10030471. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33530621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Frenotomy Modify Upper Airway Collapse in OSA Adult Patients? Case Report and Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 27;12(1):201. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010201. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36615001 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Myofunctional Therapy in Treating Sleep-Disordered Breathing: A State-of-the-Art Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 8;18(14):7291. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147291. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Measurement of Swallowing Performance Using Iowa Oral Performance Instrument: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 18;10(9):2319. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092319. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mendes FA, Marone SAM, Duarte BB, Arenas ACP. Epidemiologic profile of patients with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea in a university hospital. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Apr;18(2):142–145. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1359309. http://www.thieme-connect.com/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0033-1359309 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakker JP, Wang R, Weng J, Aloia MS, Toth C, Morrical MG, Gleason KJ, Rueschman M, Dorsey C, Patel SR, Ware JH, Mittleman MA, Redline S. Motivational Enhancement for Increasing Adherence to CPAP: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest. 2016 Aug;150(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.03.019. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/27018174 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

