Imlifidase Desensitization in Crossmatch-positive, Highly Sensitized Kidney Transplant Recipients: Results of an International Phase 2 Trial (Highdes)
- PMID: 33093408
- PMCID: PMC8294837
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003496
Imlifidase Desensitization in Crossmatch-positive, Highly Sensitized Kidney Transplant Recipients: Results of an International Phase 2 Trial (Highdes)
Abstract
Background: Highly HLA sensitized patients have limited access to life-saving kidney transplantation because of a paucity of immunologically suitable donors. Imlifidase is a cysteine protease that cleaves IgG leading to a rapid decrease in antibody level and inhibition of IgG-mediated injury. This study investigates the efficacy and safety of imlifidase in converting a positive crossmatch test to negative, allowing highly sensitized patients to be transplanted with a living or deceased donor kidney.
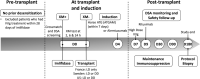
Methods: This open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial conducted at 5 transplant centers, evaluated the ability of imlifidase to create a negative crossmatch test within 24 h. Secondary endpoints included postimlifidase donor-specific antibody levels compared with predose levels, renal function, and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profiles. Safety endpoints included adverse events and immunogenicity profile.
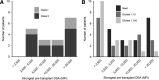
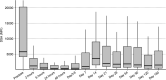
Results: Of the transplanted patients, 89.5% demonstrated conversion of baseline positive crossmatch to negative within 24 h after imlifidase treatment. Donor-specific antibodies most often rebounded 3-14 d postimlifidase dose, with substantial interpatient variability. Patient survival was 100% with graft survival of 88.9% at 6 mo. With this, 38.9% had early biopsy proven antibody-mediated rejection with onset 2-19 d posttransplantation. Serum IgG levels began to normalize after ~3-7 d posttransplantation. Antidrug antibody levels were consistent with previous studies. Seven adverse events in 6 patients were classified as possibly or probably related to treatment and were mild-moderate in severity.
Conclusions: Imlifidase was well tolerated, converted positive crossmatches to negative, and enabled patients with a median calculated panel-reactive antibody of 99.83% to undergo kidney transplantation resulting in good kidney function and graft survival at 6 mo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02790437.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures



Comment in
-
Imlifidase Shows Promise for the Most Disadvantaged Sensitized Transplant Candidates.Transplantation. 2021 Aug 1;105(8):1660-1661. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003497. Transplantation. 2021. PMID: 33093402 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hart A, Smith JM, Skeans MA, et al. . OPTN/SRTR 2017 Annual Data Report: Kidney. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(Suppl 2):19–123. - PubMed
-
- Jordan SC, Choi J, Vo A. Kidney transplantation in highly sensitized patients. Br Med Bull. 2015;114:113–125. - PubMed
-
- Statistics Report Library. Available at http://statistics.eurotransplant.org/. Accessed February 21, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

