Suppressive effects of RASAL2 on renal cell carcinoma via SOX2/ERK/p38 MAPK pathway
- PMID: 33093889
- PMCID: PMC7571372
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9280
Suppressive effects of RASAL2 on renal cell carcinoma via SOX2/ERK/p38 MAPK pathway
Abstract
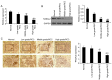
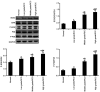
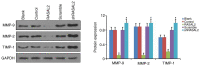
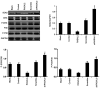
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with poor prognosis. Ras protein activator like 2 (RASAL2) protein has been previously demonstrated to serves as a tumor suppressor in a variety of malignancies. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the role of RASAL2 in RCC. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry were performed to measure mRNA and protein expression in RCC tissues, whilst immunofluorescence and western blotting were performed to evaluate protein expression in RCC cells. A Cell Counting Kit-8 and 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine staining were applied to determine cell viability, and Transwell assays were conducted to measure RCC cell invasion and migration. RASAL2 expression was identified to be downregulated in RCC tissues, which associate negatively with RCC pathological grade. Sox2 expression, in addition to ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation, were demonstrated to be increased in RCC tissues. In RCC cells, RASAL2 overexpression decreased the expression of Sox2 and the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK. Physiologically, RASAL2 overexpression decreased RCC cell viability, invasion and migration. The expression of metalloproteinase-2/9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 were also identified to be decreased and increased by RASAL2 overexpression, respectively. By contrast, RASAL2 knockdown exerted opposite effects on RCC cells compared with those observed following RASAL2 overexpression. RASAL2 expression decreased RCC cell viability, migration and invasion, which was demonstrated to be associated with the inactivation of SOX2/ERK1/2/p38 MAPK signaling. These results suggest that RASAL2 may potentially serve as a potential target for the development of novel therapeutic intervention strategies against RCC.
Keywords: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; invasion; migration; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; ras protein activator like 2; renal cell carcinoma.
Copyright: © Wang et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RASAL2, a RAS GTPase-activating protein, inhibits stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via MAPK/SOX2 pathway in bladder cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Feb 9;8(2):e2600. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.9. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28182001 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of RASAL2 promotes the proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Mar;13(3):1379-1385. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5581. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28454265 Free PMC article.
-
SPARCL1 suppresses cell migration and invasion in renal cell carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):7784-7790. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7535. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944877
-
Urokinase-induced smooth muscle cell responses require distinct signaling pathways: a role for the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Apr;41(4):672-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.01.007. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15874933
-
RASAL2 Plays Inconsistent Roles in Different Cancers.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 13;9:1235. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01235. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31799194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Tumor Progression and Cancer Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 May;10(15):e2207366. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207366. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36951547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptomic Profiles Identified the Prediction of Prognosis and Drug Sensitivity of Aminopeptidase-Like 1 (NPEPL1) for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2023 Feb 8;2023:4732242. doi: 10.1155/2023/4732242. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36816355 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDC1 is downregulated by the YY1/HDAC2 complex and controls the sensitivity of ccRCC to sunitinib by targeting the ANXA1-MAPK pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 17;41(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02460-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35974388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matalliotakis M, Velegrakis A, Laliotis A, Niraki E, Trivli A. Exacerbation of neurofibromatosis and adverse pregnancy outcome. A case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2018;45:126–128.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
