Throat Colonization and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Group a β-Hemolytic Streptococci Among Rheumatic Heart Disease Patients Attending a Cardiac Referral Hospital in Tanzania, a Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 33094103
- PMCID: PMC7527597
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2020.00057
Throat Colonization and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Group a β-Hemolytic Streptococci Among Rheumatic Heart Disease Patients Attending a Cardiac Referral Hospital in Tanzania, a Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
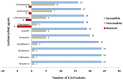
Background: Secondary prophylaxis against repeated attacks of acute rheumatic fever is an important intervention in patients with rheumatic heart disease (RHD), and it aims to prevent throat infection by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (GAS); however, its implementation faces many challenges. This study aimed to assess throat colonization, antibiotic susceptibility, and factors associated with GAS colonization among patients with RHD attending care at Jakaya Kikwete Cardiac Institute in Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania. Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study of RHD patients attending the Jakaya Kikwete Cardiac Institute was conducted from March to May 2018, where we consecutively enrolled all patients known to have RHD and coming for their regular clinic follow-up. A structured questionnaire was used to obtain patients' sociodemographic information, factors associated with GAS colonization, and status of secondary prophylaxis use and adherence. Throat swabs were taken and cultured to determine the presence of GAS, and isolates of GAS were tested for antibiotic susceptibility using Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute version 2015. Antibiotics of interest were chosen according to the Tanzanian Treatment Guidelines. Results: In total, 194 patients with RHD were enrolled, their mean age was 28.4 ± 16.5 years, and 58.2% were females. Only 58 (29.9%) patients were on regular prophylaxis, 39 (20.1%) had stopped taking prophylaxis, whereas 97 (50.0%) had never been on prophylaxis. Throat cultures were positive for GAS in 25 (12.9%) patients. Patients who stopped prophylaxis were 3.26 times more likely to be colonized by GAS when compared to patients on regular prophylaxis. Majority (96%) of GAS isolates were susceptible to penicillin, ceftriaxone, and ciprofloxacin, whereas the highest resistance (20%) was observed with vancomycin. No GAS resistance was observed against penicillin. Conclusion: The prevalence of GAS throat colonization is high among this population and is associated with stopping prophylaxis. The proportion of patients on regular secondary prophylaxis is unacceptably low, and interventions should target both patients' and physicians' barriers to effective secondary prophylaxis.
Keywords: Tanzania; acute rheumatic fever; rheumatic heart disease; secondary prophylaxis; throat colonization.
Copyright © 2020 Wangilisasi, Chillo, Kimambo, Janabi and Kamuhabwa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Throat culture positivity rate and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of beta-hemolytic streptococci in children on secondary prophylaxis for rheumatic heart disease.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 23;16(1):510. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1841-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27663649 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatic heart disease in The Gambia: clinical and valvular aspects at presentation and evolution under penicillin prophylaxis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Oct 18;21(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02308-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34663206 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negative and Beta-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Positive Pathogens Isolated from Patients in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2022 Apr 24;14(4):e24451. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24451. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35651392 Free PMC article.
-
WHO guideline on the prevention and diagnosis of rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease [Internet].Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024. PMID: 39631006 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Approaches to Improving Adherence to Secondary Prophylaxis for Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease: A Literature Review with a Global Perspective.Cardiol Rev. 2016 Mar-Apr;24(2):94-8. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000065. Cardiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 25807106 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence, Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern and Associated Factors of Streptococcus pyogenes among Pediatric Patients with Acute Pharyngitis in Sidama, Southern Ethiopia.Int J Microbiol. 2024 Sep 17;2024:9282571. doi: 10.1155/2024/9282571. eCollection 2024. Int J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39319095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. (2004) 923:1–122. - PubMed
-
- Bergmark R, Bergmark B, Blander J, Fataki M, Janabi M. Burden of disease and barriers to the diagnosis and treatment of group a beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis for the prevention of rheumatic heart disease in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2010) 29:1135–7. 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181edf475 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources