Recent cell printing systems for tissue engineering
- PMID: 33094179
- PMCID: PMC7575629
- DOI: 10.18063/IJB.2017.01.004
Recent cell printing systems for tissue engineering
Abstract
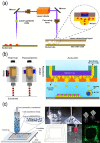
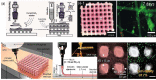
Three-dimensional (3D) printing in tissue engineering has been studied for the bio mimicry of the structures of human tissues and organs. Now, it is being applied to 3D cell printing, which can position cells and biomaterials, such as growth factors, at desired positions in the 3D space. However, there are some challenges of 3D cell printing, such as cell damage during the printing process and the inability to produce a porous 3D shape owing to the embedding of cells in the hydrogel-based printing ink, which should be biocompatible, biodegradable, and non-toxic, etc. Therefore, researchers have been studying ways to balance or enhance the post-print cell viability and the print-ability of 3D cell printing technologies by accommodating several mechanical, electrical, and chemical based systems. In this mini-review, several common 3D cell printing methods and their modified applications are introduced for overcoming deficiencies of the cell printing process.
Keywords: bioink; cell-printing; tissue engineering.
Copyright: © 2017 Lee, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest. This study was partially supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (MEST) (Grant no. NRF- 2015R1A2A1A15055305) and also a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (Grant no. HI15C3000).
Figures



References
-
- Whitaker M. The history of 3D printing in healthcare. Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England Bulletin. 2014;96:228–229. https://doi.org/10.1308/147363514X13990346756481.
-
- Griffith LG, Naughton G. Tissue engineering - Current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science. 2002;295(5557):1009–1014. https://doi.org/10.1126/ science.1069210. - PubMed
-
- Hollister SJ. Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nature Materials. 2005;4(7):518–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1421. - PubMed
-
- Whitford WG. Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting: A development parameters review. Immunome Research. 2016;12(S2):24. https://doi.org/10.4172/1745-7580.c1.004.
-
- Loo Y, Lakshmanan A, Ni M, et al. Peptide bioink:self-assembling nano fibrous scaffolds for three-dimensional organotypic cultures. Nano Letters. 2015;15(10):6919–6925. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02859. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
