Incidence, Factors, and Patient-Level Data for Spontaneous HBsAg Seroclearance: A Cohort Study of 11,264 Patients
- PMID: 33094953
- PMCID: PMC7494149
- DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000196
Incidence, Factors, and Patient-Level Data for Spontaneous HBsAg Seroclearance: A Cohort Study of 11,264 Patients
Abstract
Introduction: Spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance, the functional cure of hepatitis B infection, occurs rarely. Prior original studies are limited by insufficient sample size and/or follow-up, and recent meta-analyses are limited by inclusion of only study-level data and lack of adjustment for confounders to investigate HBsAg seroclearance rates in most relevant subgroups. Using a cohort with detailed individual patient data, we estimated spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance rates through patient and virologic characteristics.
Methods: We analyzed 11,264 untreated patients with chronic hepatitis B with serial HBsAg data from 4 North American and 8 Asian Pacific centers, with 1,393 patients with HBsAg seroclearance (≥2 undetectable HBsAg ≥6 months apart) during 106,192 person-years. The annual seroclearance rate with detailed categorization by infection phase, further stratified by hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) status, sex, age, and quantitative HBsAg (qHBsAg), was performed.
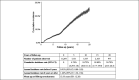
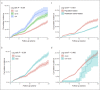
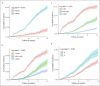
Results: The annual seroclearance rate was 1.31% (95% confidence interval: 1.25-1.38) and over 7% in immune inactive patients aged ≥55 years and with qHBsAg <100 IU/mL. The 5-, 10-, 15-, and 20-year cumulative rates were 4.74%, 10.72%, 18.80%, and 24.79%, respectively. On multivariable analysis, male (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 1.66), older age (41-55 years: aHR = 1.16; >55 years: aHR = 1.21), negative HBeAg (aHR = 6.34), and genotype C (aHR = 1.82) predicted higher seroclearance rates, as did lower hepatitis B virus DNA and lower qHBsAg (P < 0.05 for all), and inactive carrier state.
Discussion: The spontaneous annual HBsAg seroclearance rate was 1.31%, but varied from close to zero to about 5% among most chronic hepatitis B subgroups, with older, male, HBeAg-negative, and genotype C patients with lower alanine aminotransferase and hepatitis B virus DNA, and qHBsAg independently associated with higher rates (see Visual Abstract, Supplementary Digital Content 2, http://links.lww.com/CTG/A367).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
ALT to qHBsAg ratio predicts long-term HBsAg seroclearance after entecavir cessation in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol. 2024 Aug;81(2):218-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.03.022. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38527527
-
Favourable Prognosis of Patients With Untreated HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection With HBsAg < 100 IU/mL.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Feb;61(3):472-480. doi: 10.1111/apt.18383. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39523981
-
Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance and seroconversion in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic infection patients: A population-based prospective cohort.J Viral Hepat. 2018 Dec;25(12):1588-1598. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12978. Epub 2018 Sep 11. J Viral Hepat. 2018. PMID: 30112835
-
Factors Associated With Rates of HBsAg Seroclearance in Adults With Chronic HBV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):635-646.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.027. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30342034
-
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Seroclearance Rate After Stopping Nucleos(t)ide Analogues in Chronic Hepatitis B-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 May;40(5):1079-1104. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16920. Epub 2025 Mar 5. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40041970
Cited by
-
A Prospective Five-Year Follow-up After peg-Interferon Plus Nucleotide Analogue Treatment or no Treatment in HBeAg Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 May-Jun;12(3):735-744. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.12.011. Epub 2022 Jan 4. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35677522 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection.Viruses. 2021 Jun 18;13(6):1169. doi: 10.3390/v13061169. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34207458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody and quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen: Novel viral biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B management.World J Hepatol. 2024 Apr 27;16(4):550-565. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.550. World J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38689745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Profile and Seroclearance after Severe Acute Flares of Chronic Hepatitis B.Gut Liver. 2023 Mar 15;17(2):280-287. doi: 10.5009/gnl220122. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Gut Liver. 2023. PMID: 36317514 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of fatty liver on long-term outcomes in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and matched analysis of individual patient data meta-analysis.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Jul;29(3):705-720. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0004. Epub 2023 May 8. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37157776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2017. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2017.
-
- Fattovich G, Bortolotti F, Donato F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol 2008;48:335–52. - PubMed
-
- Seto WK, Lo YR, Pawlotsky JM, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018;392:2313–24. - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Wang XW, Chen L, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016;43:1253–61. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, et al. Spontaneous seroclearance of hepatitis B seromarkers and subsequent risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2014;63:1648–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

