Seropositive Prevalence of Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China
- PMID: 33095246
- PMCID: PMC7584925
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.25717
Seropositive Prevalence of Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China
Abstract
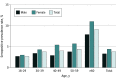
This cross-sectional study examines the seropositive prevalence of antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Wuhan, China, by sex and age group.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
Association of Public Health Interventions With the Epidemiology of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Wuhan, China.JAMA. 2020 May 19;323(19):1915-1923. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6130. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32275295 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous