Tafazzin Mutation Affecting Cardiolipin Leads to Increased Mitochondrial Superoxide Anions and Mitophagy Inhibition in Barth Syndrome
- PMID: 33096711
- PMCID: PMC7589545
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9102333
Tafazzin Mutation Affecting Cardiolipin Leads to Increased Mitochondrial Superoxide Anions and Mitophagy Inhibition in Barth Syndrome
Abstract
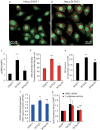
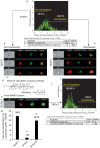
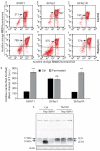
Tafazzin is a phospholipid transacylase that catalyzes the remodeling of cardiolipin, a mitochondrial phospholipid required for oxidative phosphorylation. Mutations of the tafazzin gene cause Barth syndrome, which is characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction and dilated cardiomyopathy, leading to premature death. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the cause of mitochondrial dysfunction in Barth syndrome remain poorly understood. We again highlight the fact that the tafazzin deficiency is also linked to defective oxidative phosphorylation associated with oxidative stress. All the mitochondrial events are positioned in a context where mitophagy is a key element in mitochondrial quality control. Here, we investigated the role of tafazzin in mitochondrial homeostasis dysregulation and mitophagy alteration. Using a HeLa cell model of tafazzin deficiency, we show that dysregulation of tafazzin in HeLa cells induces alteration of mitophagy. Our findings provide some additional insights into mitochondrial dysfunction associated with Barth syndrome, but also show that mitophagy inhibition is concomitant with apoptosis dysfunction through the inability of abnormal mitochondrial cardiolipin to assume its role in cytoplasmic signal transduction. Our work raises hope that pharmacological manipulation of the mitophagic pathway together with mitochondrially targeted antioxidants may provide new insights leading to promising treatment for these highly lethal conditions.
Keywords: Barth syndrome; apoptosis; autophagy; cardiolipin; electron transport; mitochondria; tafazzin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiolipin remodeling by TAZ/tafazzin is selectively required for the initiation of mitophagy.Autophagy. 2015 Apr 3;11(4):643-52. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1023984. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25919711 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of mitophagy ameliorates cardiomyopathy in Barth syndrome.Autophagy. 2022 Sep;18(9):2134-2149. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.2020979. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 34985382 Free PMC article.
-
Barth syndrome: cellular compensation of mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis inhibition due to changes in cardiolipin remodeling linked to tafazzin (TAZ) gene mutation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1832(8):1194-206. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23523468
-
The Function of Tafazzin, a Mitochondrial Phospholipid-Lysophospholipid Acyltransferase.J Mol Biol. 2020 Aug 21;432(18):5043-5051. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.03.026. Epub 2020 Mar 29. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32234310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Barth syndrome: cardiolipin, cellular pathophysiology, management, and novel therapeutic targets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Mar;476(3):1605-1629. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-04021-0. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33415565 Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium arsenite and arsenic trioxide differently affect the oxidative stress of lymphoblastoid cells: An intricate crosstalk between mitochondria, autophagy and cell death.PLoS One. 2024 May 10;19(5):e0302701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302701. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38728286 Free PMC article.
-
Tafazzin-Deficient Zebrafish Display Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Neutropenia, and Metabolic Defects Without Myopathy.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 24:rs.3.rs-5960642. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5960642/v1. Res Sq. 2025. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23679. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07843-4. PMID: 40313767 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Current Knowledge on the Role of Cardiolipin Remodeling in the Context of Lipid Oxidation and Barth Syndrome.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 27;9:915301. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.915301. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35693555 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic basis of inherited neutropenias.Br J Haematol. 2024 Jan;204(1):45-55. doi: 10.1111/bjh.19192. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Br J Haematol. 2024. PMID: 38049194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in Islet Biology: A Review With Patient Perspectives.Can J Diabetes. 2023 Mar;47(2):207-221. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2022.11.003. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Can J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 36481263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barth P., Scholte H., Berden J., Moorsel J.V.D.K.-V., Luyt-Houwen I., Veer-Korthof E.V., Van Der Harten J., Sobotka-Plojhar M. An X-linked mitochondrial disease affecting cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and neutrophil leucocytes. J. Neurol. Sci. 1983;62:327–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(83)90209-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ronvelia D., Greenwood J., Platt J., Hakim S., Zaragoza M.V. Intrafamilial variability for novel TAZ gene mutation: Barth syndrome with dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure in an infant and left ventricular noncompaction in his great-uncle. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012;107:428–432. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.09.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

