Is IDDSI an Evidence-Based Framework? A Relevant Question for the Frail Older Population
- PMID: 33096747
- PMCID: PMC7709687
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics5040082
Is IDDSI an Evidence-Based Framework? A Relevant Question for the Frail Older Population
Abstract
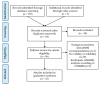
To delay impacts of aging, optimal nutritional status is essential. Several factors can reduce food intake, such as isolation, income, and cognitive/physical decline. Additionally, chewing and swallowing difficulties, or dysphagia, often disrupt the ability to consume life-long favorite dishes. Food and liquids could require modification of texture or consistency to ensure a comfortable or safe swallow. The food industry, foodservices facilities, and caregivers need quality control benchmarks to provide adequate nourishment and meet these new feeding challenges. The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) is proposing the IDDSI framework and testing methods to describe food used in nutritional care plans to circumvent dysphagia and improve communication among caregivers. This systematic review assesses the validity and reliability of the IDDSI testing methods using the Consensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN). Two publications presented content validity whereas 19 publications looked at construct validity or reliability for the IDDSI testing methods. One study was conducted in older adults presenting dysphagia. This review concludes that there is insufficient evidence to recommend the IDDSI testing methods. Further research, conducted with robust methodological design and reporting, is needed to develop and assess nutritious adapted food for frail older populations.
Keywords: COSMIN; IDDSI; dysphagia; metrological qualities; nutrition; older adults; swallowing; texture modified food; thickened liquids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ambali A. Preventive geriatrics—A way towards active ageing. In: Shankardass M., editor. Ageing Issues and Responses in India. Springer; Singapore: 2020. pp. 25–43. - DOI
-
- Nettore I.C., Ungaro P., Macchia P.E. Food and nutrition as prime environmental factors. In: Teperino R., editor. Beyond Our Genes: Pathophysiology of Gene and Environment Interaction and Epigenetic Inheritance. Springer Cham; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2020. pp. 3–16. - DOI
-
- Wakabayashi H. Role of nutrition and rehabilitation in the prevention and management of sarcopenia and frailty. In: Kato A., Kanda E., Kanno Y., editors. Recent Advances of Sarcopenia and Frailty in CKD. Springer; Singapore: 2020. pp. 117–138. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources