Treatment with Luteolin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Periodontal Diseases in Rats
- PMID: 33096800
- PMCID: PMC7590181
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8100442
Treatment with Luteolin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Periodontal Diseases in Rats
Abstract
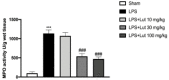
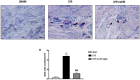
Periodontitis is a dental disease that produces the progressive destruction of the bone surrounding the tooth. Especially, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is involved in the deterioration of the alveolar bone, inducing the release of pro-inflammatory mediators, which cause periodontal tissue inflammation. Luteolin (Lut), a molecule of natural origin present in a large variety of fruits and vegetables, possess beneficial properties for human health. On this basis, we investigated the anti-inflammatory properties of Lut in a model of periodontitis induced by LPS in rats. Animal model predicted a single intragingival injection of LPS (10 μg/μL) derived from Salmonella typhimurium. Lut administration, was performed daily at different doses (10, 30, and 100 mg/kg, orally), starting from 1 h after the injection of LPS. After 14 days, the animals were sacrificed, and their gums were processed for biochemical analysis and histological examinations. Results showed that Lut (30 and 100 mg/kg) was equally able to reduce alveolar bone loss, tissue damage, and neutrophilic infiltration. Moreover, Lut treatment reduced the concentration of collagen fibers, mast cells degranulation, and NF-κB activation, as well as the presence of pro-inflammatory enzymes and cytokines. Therefore, Lut implementation could represent valid support in the pharmacological strategy for periodontitis, thus improving the well-being of the oral cavity.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; dental diseases; flavonoids; lipopolysaccharide; luteolin; periodontitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Gasner N.S., Schure R.S. Periodontal Disease. StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

